Before our school went on winter break, my science class started learning about cells and how they multiply. We started off learning about Mitosis which was more difficult to understand that I thought.
Adding to that we also learned about DNA and the cell cycle. The three stages of the cell cycle that we learned about were Interphase , Mitosis and Cytokinesis.
Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle, it is divided into three parts, the first is growth and preparation, next is DNA replication and the last one is continued growth and preparation.
Before the cells could go through the cell cycle they have to first have enough nutrients, the DNA should replicate and it should not be damaged. The DNA will not replicate properly if it is damaged. It goes through three steps.
Mitosis is the process where the contents in the cell’s nucleus divide. The division will result in two daughter nuclei, each identical to each other. Mostly the daughter nuclei are also identical to the parent but sometimes they do alter.
The way we have memorized the mitosis stages are using PMAT as the acronym.
Prophase is the stage where the nucleus disappears and the spindle fibres move to either side of the cell. Metaphase is when the chromosomes align on the middle of the cell. Anaphase is where cell chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by spindle fibres and Telophase is the final stage in which the spindle fibres and nuclear form around each daughter cell.
Cytokinesis is where the cell divides and form the two different daughter cells.
(Please note that daughter cells from mitosis have the same number of chromosomes as each other and as the parent.)
Meiosis might seem similar to Mitosis but there are lots of differences, one is that when the meiosis process is finished you are left with 4 non identical cells. Meiosis also requires two parents instead of mitosis which only required one.
Prophase 1- Homologous chromosomes pair up and the non sister chromatids exchange their genetic material. This is also knows as crossing over.
Metaphase 1- Homologous chromosomes pair up at the equator of the cell.
Anaphase 1- The chromosomes separate and are pulled to the opposite poles.
Telophase 1- One chromosome from each homologous pair is at each pole of the cell.
^^^The second stage of meiosis is the same steps of mitosis only that it is two in the beginning and therefore the results will be four.^^^
——–
Asexual Reproduction (Mitosis)
Asexual reproduction is when there is only one parent. It is naturally how clones are formed to help in agriculture in order to develop different things. Different examples are:
Budding– When several areas of an organism go through repeated mitosis to form an identical organism. Example is Hydra.
Binary Fission– When single cell organisms split into identical copies. Example is Bacteria reproducing.
Fragmentation– When a part of an organism breaks off and that piece grows into a clone of the original. Example is Starfish.
Vegetative Reproduction– Special cells in the plant that develop into structures that form new plants that are identical to the parent. Example is Potatoes.
Spore Formation– Single cells that grow into a whole new organism. Example is Fungi.
Sexual Reproduction (Meiosis)
Sexual reproduction is when there are two parents. It require the parents to bring two different gametes together for the fertilization to happen. This process brings to identical gametes together to form a new organism. It has three stages: Mating, Fertilization and Development.
Mating is when the gametes arrive in the same place. Lots of animals have mating seasons in which they meet but in general every mammal has a different time for when they do mate.
We went through a gallery walk in our class to learn more about the different kinds of fertilization for Sexual Reproduction.
External Fertilization- This process is common for animals that live underwater and it is when a sperm and egg cell unite outside of the parent’s bodies. This happens when a sperm cell comes in contact with the same species egg cell. Example is Fishes.
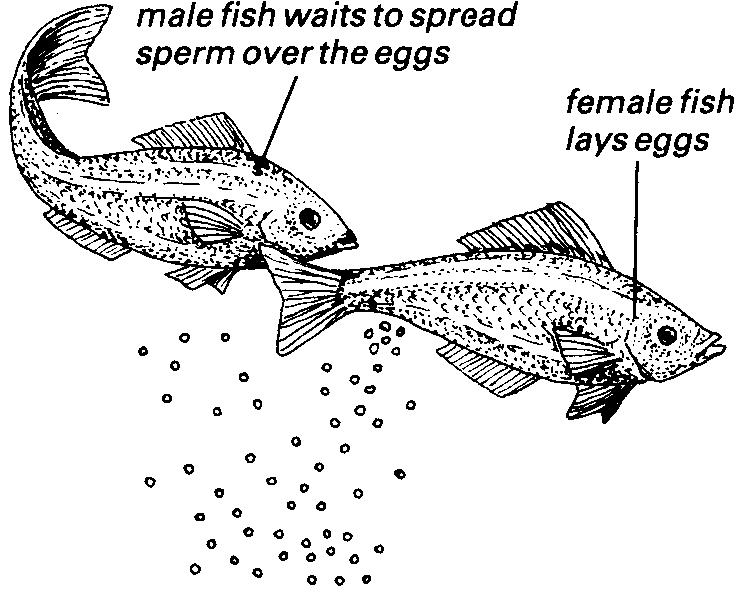
Internal Fertilization- This is when the sperm cell meets the egg cell inside the female and that’s where the fertilization happens. In this fertilization the embryo grows and is nourished in the mother’s body. Example is Humans.
Pollination- This is when the pollen from the male parts of the cells which contain sperm go over to the female part of the plant where there are eggs. Example is flowers.

Pollen Transport- Some plants do not have petals therefore the way they transport their pollen is by releasing it the air to be carried out to the female reproductive parts or other flowers. Example is Douglas Fir tree.
Embryonic Development- This is the first two months of development after fertilization.
Fetal Development- This is put into three trimesters, each trimester approximately 3 months long. In the first trimester the baby is developing it’s organs and the brain and spine are forming. The second trimester is for growth and it is when the gender is known and also the baby can open it’s eyes. The last trimester is just for continued growth and the baby is gaining weight getting ready to be born.

—
Asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction have different advantages(pros) and disadvantages(cons):
Advantages for Asexual reproduction are that it doesn’t take much energy to find a mate and many off springs are produced.
Advantages for Sexual reproduction are that the off springs created are protected well as an embryo and they are not affected by the same diseases which can result in the species living longer.
Disadvantages for Asexual reproductions are that the off springs may all die at a certain temperature and if one dies because of a certain disease all will because they are all identical.
A disadvantage for sexual reproduction is that it takes more energy to find a mate.
~~~~~~~~~~~~
Overall we learned a lot about biology and I think it was a very fun chapter!
****Photo credits to the photos are unknown to me but I got them from our OneNote class notebook




