- Biomes in the Arctic:
-subarctic
Churchill, Manitoba, Canada
The ground in this biome is covered in permanent ice, so there might only grow some lichens, which are strongy built because they have to resist the strong arctic winds.
- Biomes in the Cordillera
- Coast and Interior Forest
Stanley Park, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Due to the location close to the coast the Coast and Interior Forest gets lots of precipitation. Only in BC there are 60 Million Hectares covered by Coast and Interior Forests, that is about two thirds of the land-mass.
- Tundra
The ground in this biome is covered in permanent ice, so there might only grow some lichens, which are strongy built because they have to resist the strong arctic winds.
Grassland
The dry climate allows not many plants to grow, which is the reason why there is a small amount of trees, while most of the land-mass is covered in grasses, which can grow up to 1,5 meters high.
- Parkland
Parkland in the South Western corner of Alberta, Canada
This biome is between Forest and Grassland. There are some trees and some grass covered areas as you can see in the picture.
- Coniferous Forest
Manning Provincial Park, Southwestern BC, Canada
In this biome there are only Coniferous Trees, or how many people call them evergreen trees. Those trees never lose their leaves, even in Winter they keep them.
- Open Woodland
Graves Island Provincial Park, Nova Scotia
The tree population in this biome is not really dense, which provides good access to lot of sunlight and little amount of shadow.
- Biomes in the Canadian Shield
- Tundra
The ground in this biome is covered in permanent ice, so there might only grow some lichens, which are strongy built because they have to resist the strong arctic winds.
- open woodland
- coniferous forest
- mixed forest
Algoma Highlands, Ontario, Canada
In this biome there is enough precipitation for big trees to grow. Here we can see both coniferous and deciduous trees.
- Biomes in the Interior Plains Regiom
- Parkland
- Grassland
- Coast and Interior Forest
- Tundra
- Coniferous Forest
- Biomes in the St. Lawrence Lowlands Region
- Mixed Forest
- Coniferous Forest
- Biomes in the Appalachian Region
- Open Woodland
- Mixed Forest
- Coniferous Forest
How were all the Physiographic Regions formed?
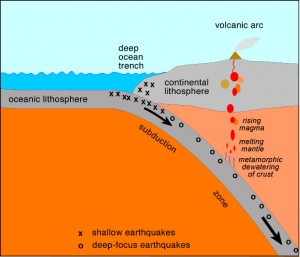
How were the Cordilleras formed?
The Pacific plate subducting under the North American plate caused magma to rise into the earth surface, which then cooled down and forme the Coast Mountains. Those mountains are an important part of the Cordillera region.
How was the Interior Plains region formed?
500 Million years ago that region was covered by shallow seas. The rivers that were flowing into those seas deposited layer over layer of sedimentary rock. When the seas drought out the sedimentary rock became the surface of the Interior Plains region and is now mostly covered in grass.
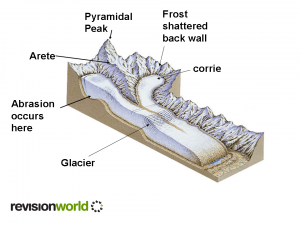
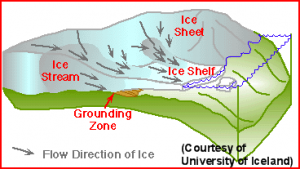
How was the Arctic regions formed?
During the last Ice Age, when Canada was completely covered by giant glaciers, there were Glaciers flowing in all directions in the Arctic region. The ground was compressed under the huge weight of the glaciers, that is why ist is still so flat.
How was the Canadian Shield region formed?
The Canadian Shield was formed by plate tectonic movements, volcanic eruption and sedimentary deposits. It got its flat landscape from glacial erosion and glacial incursion.
How were that St. Lawrence Lowlands formed?
This region was like all the other regions formed by glacial erosion, but also by rivers and deposits. The river flowing through tis region left deposits and carved out river valleys. That is how the St. Lawrence Lowlands were formed. The giant lakes in this region were formed by melting glaciers.
How was the Appalachian Region formed?
The Appalachian region is located on the coast where the continental plate and the oceanic plate subduct. That formed the hills. The reason why the hills are flat and round is that the giant glaciers carved off the tops and left the round mountains.