Trigonometry, as the name might suggest, is all about triangles.
More specifically, trigonometry is about right-angled triangles, where one of the internal angles is 90°. Trigonometry is a system that helps us to work out missing or unknown side lengths or angles in a triangle.
A right-angled triangle has a single right angle. By definition, that means that all sides cannot be the same length. A typical right-angled triangle is shown below.

- The right angle is indicated by the little box in the corner.
- The other angle that we (usually) know is indicated by θ (theta).
- The side opposite the right angle, which is the longest side, is called the hypotenuse.
- The side opposite θ is called the opposite.
- The side next to θ which is not the hypotenuse is called the adjacent.
Introducing Sine, Cosine and Tangent:
There are three basic functions in trigonometry, each of which is one side of a right-angled triangle divided by another.
The three functions are:
| Name | Abbreviation | Relationship to sides of the triangle |
| Sine | Sin | Sin (θ) = Opposite/hypotenuse |
| Cosine | Cos | Cos (θ) = Adjacent/hypotenuse |
| Tangent | Tan | Tan (θ) = Opposite/adjacent |
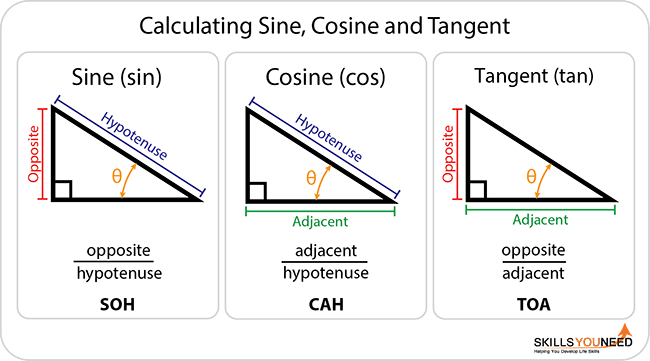
You may find it helpful to remember Sine, Cosine and Tangent as SOH CAH TOA.
Remembering trigonometric functions can be difficult and confusing to begin with. Even SOH CAH TOA can be tricky. You could try making up a funny mnemonic to help you remember. Just keep each group of three letters in the same order.
For example, TOA SOH CAH could be ’The Old Archaeologist Sat On His Coat And Hat’.
sources
https://www.skillsyouneed.com/num/trigonometry.html



