Archaebacteria
-single-celled microorganism; don’t have a nucleus.
-very similar to Eubacteria but they belong to different domains (bacteria-domain bacteria, Archaebacteria- Archea) Archea have a membrane which is more stable than bacteria’s, and it helps archaea to survive at extreme temperature (e.g: volcano) and p.h environment
Nanoarchaeum equitans
- a type of marine archaea
- known as the smallest known archaeon
- discovered in 2002
Lokiarchaeota

- host of the interaction at the origin of mitochondria
- Not much information is discovered about it
Eubacteria
- prokaryotic
- commonly found in human daily life than Archaebacteria
- causing diseases
- lack mitochondrions or chloroplasts
- have a rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan
- undergo asexual binary fission when reproducing
Blue-green bacteria (Cyanobacteria)
- important to aquatic communities (they provide oxygen)
- obtain their energy through photosynthesis
- have internal membrane
Spirochaetae
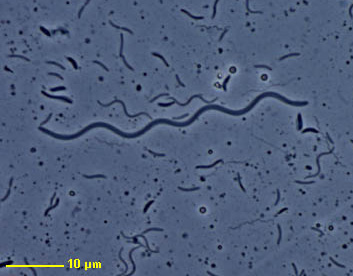
- a flexible spirally twisted bacterium
- causes syphilis
Protista
- can sexually/asexually reproduce
- most of them are unicellular
- includes organisms as algae, slime, molds, and protozoa.
- include both autotrophic and heterotrophic forms.
marimo (Aegagropila linnaei)

- also known as a mossball
- usually found on the shady side of rocks or in lakes
- takes almost a century to grow in a size of a baseball
Wakame(Undaria pinnatifida)
- good for health (fucoxanthin helps to burn the fat cells)
- lots of nutrients
- Seaweed has been classified as a plant in the past, but genetic testing has shown that the appearance of a seaweed plant is an extrovertive trait that has developed apart from the plant.
[Fungi]
- include mushrooms, yeasts, molds, rusts, smuts, puffballs, truffles, morels, and molds
- live everywhere in the air, in water, on land, in soil, and on or in plants and animals
- appear like plants but are closely related to animals
- eukaryotic
- grows on dead leaves and roots in grasslands
- produce rings of fruiting bodies or mushrooms
Basidiomycetes
- cause diseases in animals and also humans
- obtain nutrition by decaying dead organic matter
- Basidiomycota play a significant role in the carbon cycle
- some Basidiomycota produce deadly toxins
Microsporidia
- caused diseases (Enterocytozoon, Encephalitozoon, Nosema, Pleistophora, Trachipleistophora, Vittaforma, Brachiola)
- spore-forming organism
- found in patients with infected immune system such as HIV
- beside that, it is important parasites in fisheries,veterinary medicines and pest management
Plantae
- mainly multicellular
- Eukaryotics
- autotrophic mode of nutrition.
- sexual reproduction
- most of them synthesis their own food with the help of solar energy (photosynthesize)
Daffodil (Narcissus poeticus)
- change the juice of daffodils and use it to treat swelling.
- native to Korea, China, Japan and the Mediterranean Sea.
- can grow in the winter
Sunflower Helianthus)
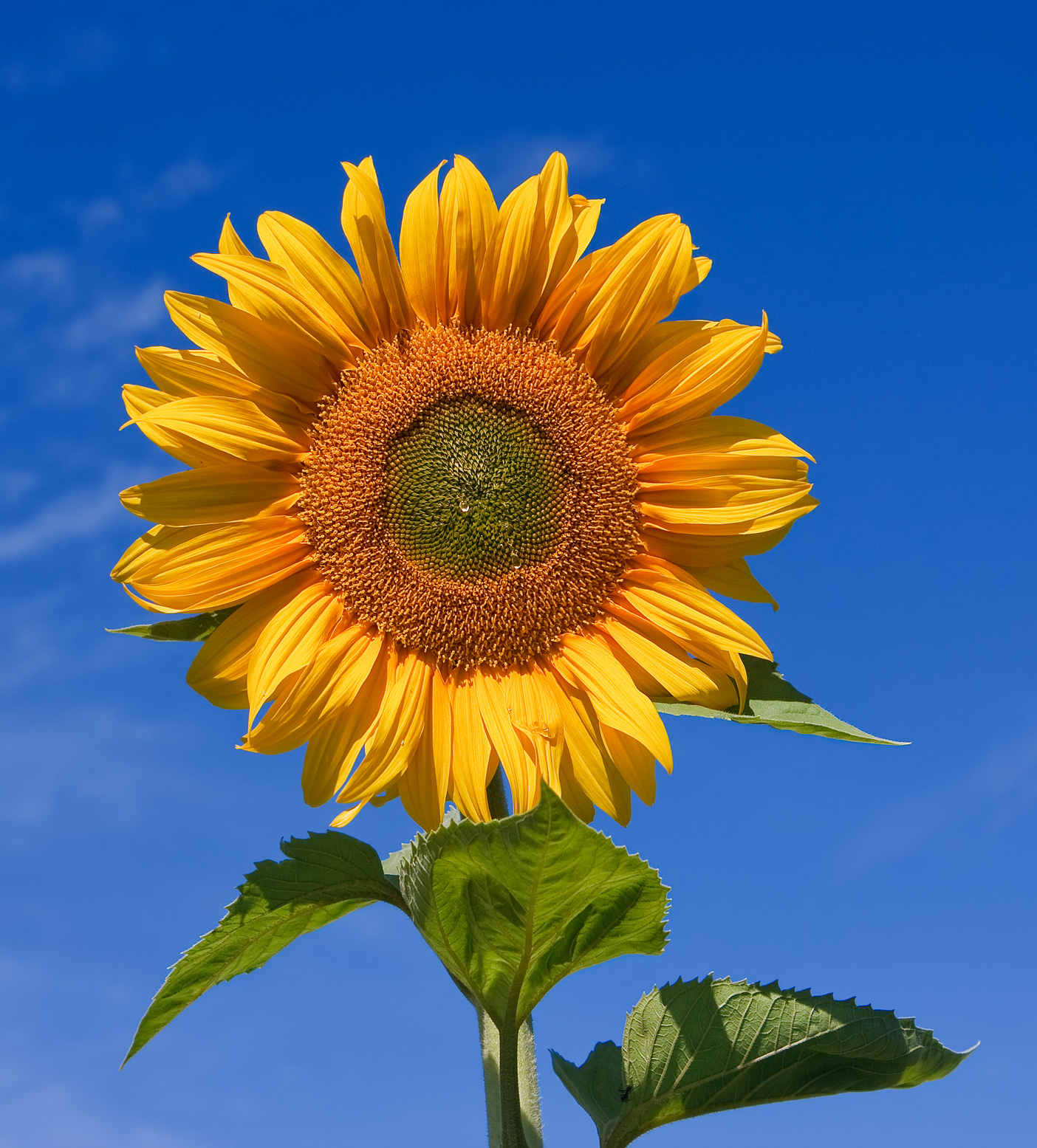

- can obtain seeds / oil
- can grow to the height of 300cm
- always face the sun when they are still growing, but stop when they begin blooming
Animalia.
- Multicellular organism
- no cell wall
- Eukaryotic cells
- higher level of tissue organization
- sexual reproduction
- has to obtain nutrients from another species
Red panda
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/49388585/16071828377_85109fdee4_o.0.0.jpg)
- also known as lesser panda
- classified as endangered
- although it is called a panda, it is not closely related to the giant panda
- has a very long tail. (bigger than the body)
- lives in temperate forests
- solitary except during mating season
Black mamba
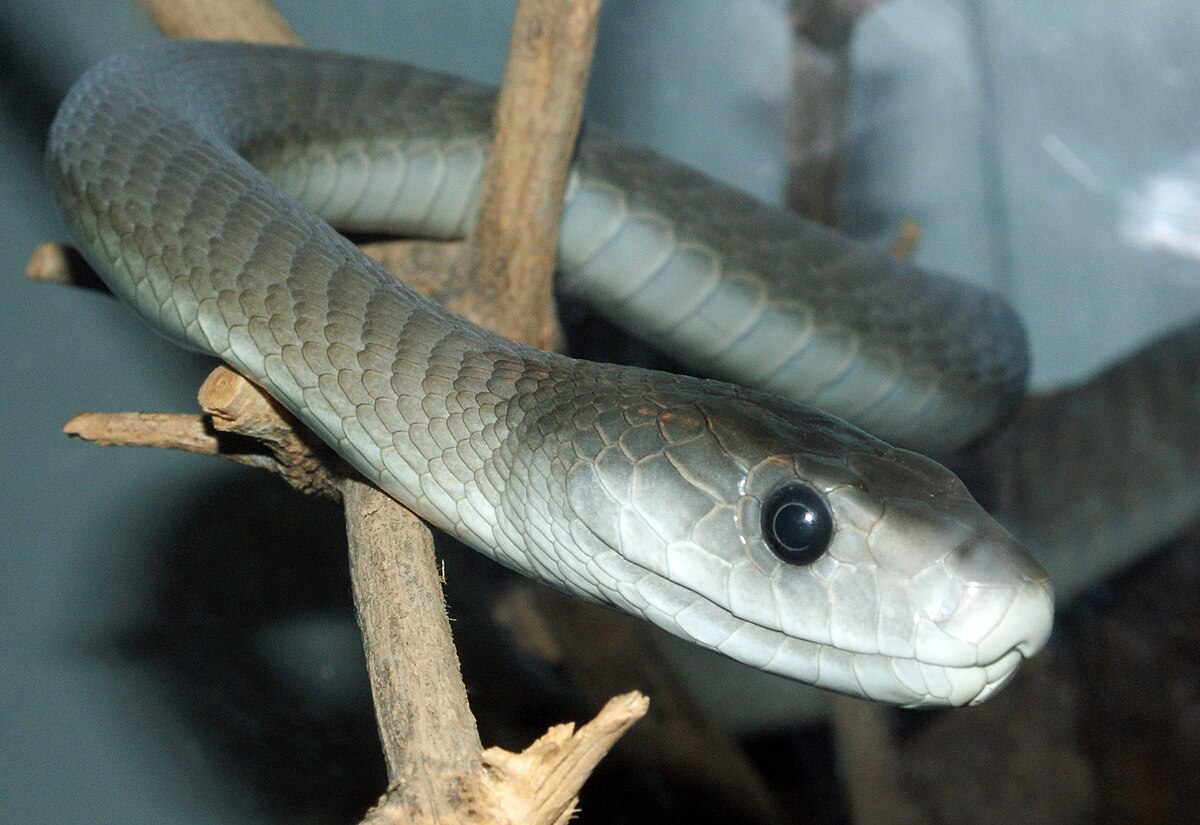

- native to Africa
- longest species of snakes ; the largest Black mamba reported was 4.5m (14.8ft)
- unpredictable behavior
- black mamba venom can poison a mouse in 4.5 minutes (extremly toxic)
- known as the most dangerous animal in Africa – Black mamba’s bite is called “kiss of death”
