Sexual Reproduction and Asexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction has Variation and it requires two parents. Every offspring is different unless you have identical twins. Some pros to sexual reproduction is, if there is a negative mutation it may not effect the offspring, and they will not have to compete for food and space because large colonies are not produced at one time.
Sexual Reproduction is when reproductive cells fuse together. This is called gametes.For this to happen it requires a males sperm and a females egg.
The sperm fertilizes an egg and creates an embryo. The embryo will grow and get nourished inside of the females body.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction only requires one parent. The offspring is an identical clone to the parent. With asexual reproduction there is no variation. Some pros to asexual reproduction is that large colonies can be produced at one time when conditions are favourable. Large colonies can win over other organisms with nutrients and water. Asexual reproduction is used with plants and injured organisms as well as other things. There are also several different types of asexual reproduction. In class we talked about the five types.
Budding- Budding is when parts of cells go through repeated mitosis, so it creates an identical organism. An example of this that we talked about in class, is yeast cells.

Binary Fission- Binary Fission is when a singular cell divides into an identical copy of itself. An example of this that we used in class was a bacteria cell.

Fragmentation– Fragmentation is when part of an organism breaks off because of injury and the part grows into a new cloned organism. We talked about the example a starfish.

Vegetation Reproduction- Vegetation Reproduction is when special types of cells in plants grow and form identical new cloned plants. They can do this through bulbs, sprouts, and runners. An example that we talked about in class are Strawberry plants.
Spore Formation- Spore Formation is when single cells grow into an entire new organism. We talked about Fungi as an example.

Meiosis and Mitosis
Mitosis
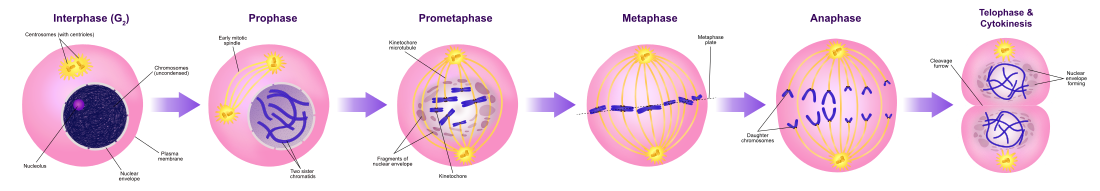
Mitosis is a stage in the cell cycle. There are four different stages in mitosis. The four stages are Prophase,Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. You can remember this by thinking of PMAT.
Prophase: The spindle fibres form and the nucleus disappears.
Metaphase: The chromosomes get pulled and line up at the middle of the cell (the equator) by the spindle fibres. I remember this by thinking meta is middle.
Anaphase: The chromosomes get pulled away from each other and away from the centre.
Telophase: The spindle fibres disappear and new nuclear membranes are formed around each separate sets of chromosomes.
Meiosis
Meiosis has eight steps instead of four steps like mitosis. Meiosis also makes double the amount of cells than mitosis makes. Meiosis is very similar to mitosis but it does have some major differences These are the steps of meiosis…
Prophase I: The chromosomes bond together with their copies and become X chromosomes. They recombine and crossover with Homologous.
Metaphase I: The homologous Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell by spindle fibres.
Anaphase I: The homologous chromosomes get pulled to the opposite sides of the cell by the spindle fibres.
Telophase I: Each side of the cell has one chromosome.
Prophase II: Each cell has a homologous chromosomes pair.
Metaphase II: X chromosomes line up at the centre of the cells.
Anaphase II: the sister chromosomes are pulled to opposite sides of the cell and they are no longer sister chromosomes. They are just called chromosomes because they split.
Telophase II: Spindle fibers disappear and each pair of chromosomes have a nuclear membrane that surrounds them.

Organism Growth
External Fertilization
External fertilization is done through spawning. An example of spawning are fish. The male fish releases its sperm when a female fish releases its egg. This happens under water to protect the egg. Because the egg is not inside of the female she is not protecting it so there is a high chance that the egg could get damaged.
Internal Fertilization
Internal Fertilization leads to embryo development. There are three different stages. The stages are called trimesters.The fetus is developing in these trimesters. in the first trimester It develops its organ systems and you can almost see what the gender of the fetus is. In the second trimester the babies eyes start to open and you can start to feel the baby kicking. And it the third trimester the baby grows and develops. At the end of nine months the baby is ready to come out of the female.
Sources
