Category: Uncategorized
What Darwin Never Knew
How did the discovery of DNA prove that Darwin’s theory of evolution was correct and how does it change the way we view evolution today and into the future?
Darwin’s book on evolution was based on natural selection and how organisms will have a variety of changes in their physical and/or behavioural traits over a period of time due to their environment, and the organisms surrounding it. These changes will help the organism survive in it’s habitat. This goes along with when Darwin was looking at the finches and realized they all had different physical and behavioural characteristics. It helped him to realize that even though they are the same species, they will all have very different and unique DNA, and it all depends on the animal’s role in it’s environment and the things it need to do to survive. Over long periods of time these adaptions will be noticeable and will assist the organism in it’s field. This has helped with and altered the way we view evolution today because human’s realized that all species of animals, reptiles, and even plants, are connected in some very important way. Some examples of this is animals acquiring wings to help them fly, feathers or fur to keep them warm, large beaks for food and defense, and webbed feet for easier transportation through water. Because of Darwin’s theory and discoveries, we have been able to make many more of them and explore so many new ideas with evolution and how it is still in process today.
Organisms in Kingdoms Examples
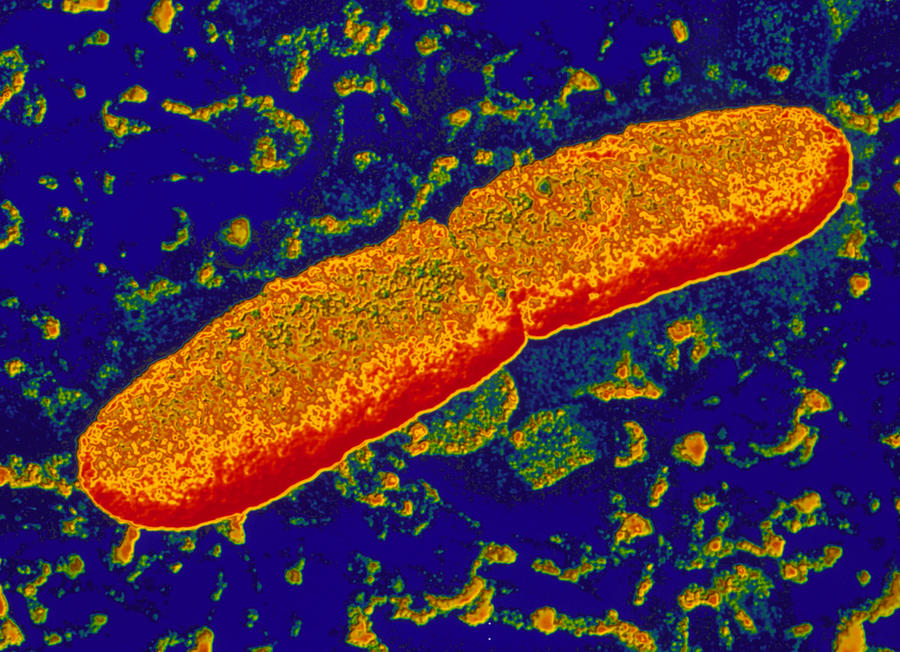
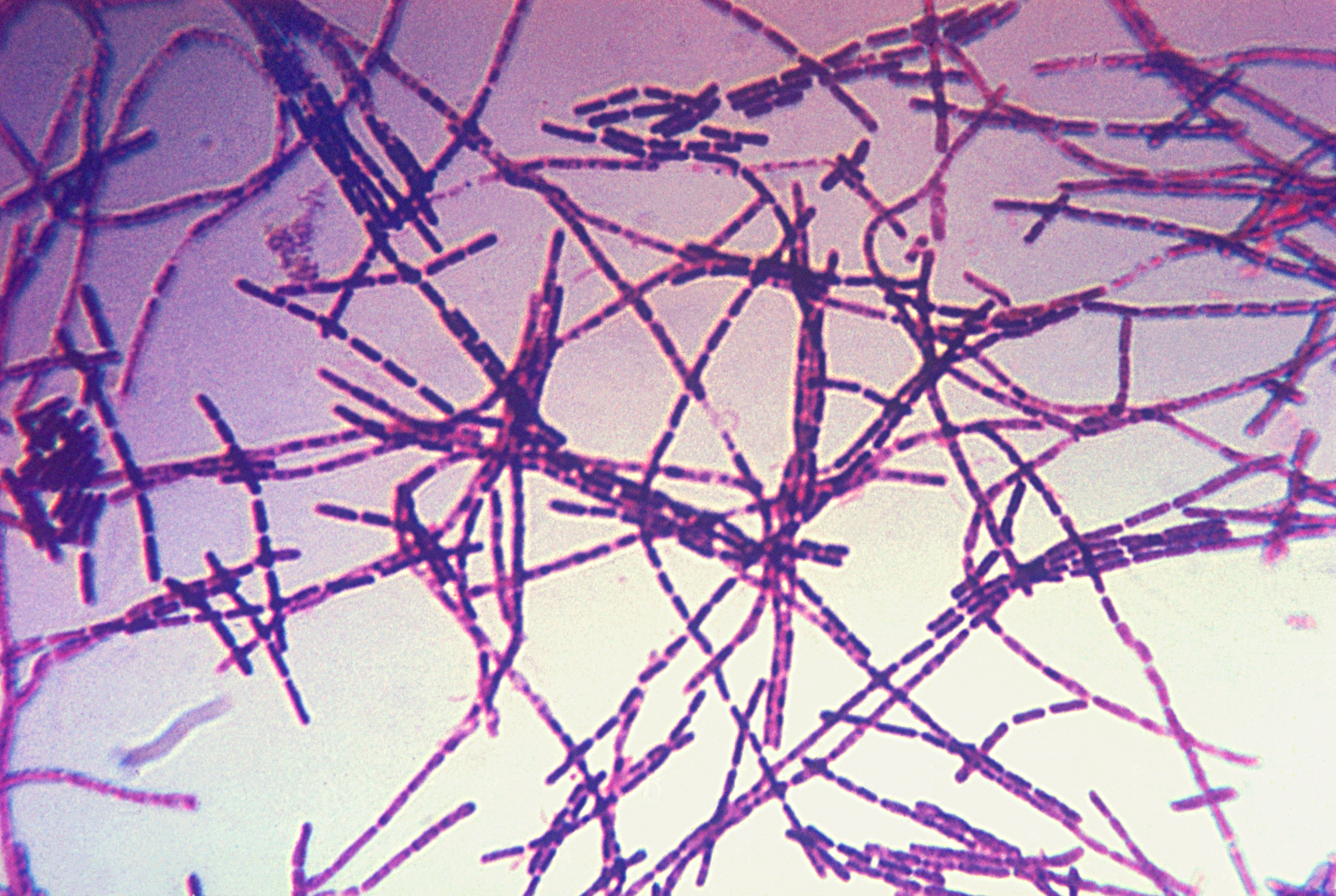
Eubacteria Kingdom
Yersinia pestis – This example of eubacteria can have a deadly effect on humans and animals causing and spreading “the plague” (Bubonic Plague). The Y. Pestis has three main forms; pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic plagues.






Bag Of Change
Chemical A: Chemical A was kind of a thin, white, powdery substance. After the chemicals were mixed together, chemical A turned into foamy yellow – white substance.
Chemical B: Chemical B were white pellets, almost identical to nerds (the candy) with no colour. Most of chemical B completely disappeared, when only 4 or 5 pellets, shrunk to the size of a crumb.
Chemical C: Chemical C was a blue liquid that was basically blue food colouring. After we mixed them together, it was mainly with chemical A to make the foamy substance.
After I mixed the chemicals together, the substance got very hot, but after about 5 minutes of continuously massaging it, it got very cold. Chemical B almost completely disappeared, and chemicals A and C turned in a white, foamy mixture.
Chemical Change – When the substance has changed colour, matter (liquid – solid), etc.
Physical Change – When only the look of something changed. (ripped or crumpled pieces of paper.)
In this experiment, there were many chemical changes such as, it changed from white to blue to yellow, the little pellets and the powder change to a foamy substance, and the mixture went from hot to a cold temperature.
Mutant Bees
For Mutation A, the bee had 4 antennae instead of 2, like on the original bee. On Mutation B, it had no wings. And for the last mutation, it was a little harder to see than the others. It’s stinger was pointing down towards the ground instead of up, like the original bee.
I thing the first bee had a beneficial mutation. Since bees use their antennae for senses like taste, smell and touch, I think having double the amount of antennae would either make the senses stronger, or let you taste, smell or touch more things at a time. Mutation B bee definitely had a negative mutation because the only thing that not having wings would do is not let you fly, and bees need to be able to fly because they need to get places fast and there’s basically no other way of transportation. I think the bee with the mutation of it’s stinger pointing down is not affected because I don’t think that would change any way you sting people. Yes, maybe the bee with have to point it’s body down a little more while stinging a person but that is not necessarily a bad thing.
Yes, I do think that this activity help with my understanding of mutation because it clearly shows the differences in the bees and is easy to describe.
