Ask:
1.What area of water works best for tidal energy turbines and machines to power in? Is there a specific type of water that allows them to improve and work faster?
2. What countries have better access to tidal energy and have implanted it into their ecosystem?
3. What is the process of renewable energy being used and cycled through tidal machines?
4. How is tidal energy a useful energy production and what benefits does it display?
5. How long does it take for tidal energy turbines to be built and implanted into the water?
6. Who designed a tidal energy turbine and came up with this helpful source of energy? When was it invented?
7. How can our country (Canada) use tidal energy in a useful way and what benefits can this make to our waters, air and environment?
8. How is Tidal energy better and more efficient in our waters compared to other sources of energy such as Wave energy?
9. What materials are used in tidal energy turbines and how much money do tidal energy machines cost?
10. Are there different models of turbine machines? How are they different from each other? Do they produce the same benefits?
This is an image of Tidal energy machines implanted along the water

“FLOWLIGHT – Renewable Energy Product” by Shane Molloy is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
Acquire:
What is Tidal energy?
Tidal energy is an energy source that can be renewed and is moved by the force of the oceans flow, current and tidal ranges. Tidal energy uses the pull of gravity from the earth to create energy. It is in the form of many different machines and works to convert the energy from the tide into forms of natural electricity and power.
When was Tidal energy invented?
Tidal energy was first recognized and established on November 26, 1996. Charles de Gaulle; the president of France was the first person to open a power station in Brittany, France on the Rance Estuary. This new power source was made by an electric company in France called EDF. It was placed on the creek of Saint-Malo on the Atlantic ocean as there are many tide and ocean currents in that area. This power source has 24 fast turbines to convert the oceans energy into power for the country. This power station has been successful and the country is still using it for helpful and renewable resources. It was very costly to built, but France has gained 600 million kilowatt of electricity yearly. France uses this energy opposed to other energies that involve the wind or air. It is much more dependable and tides are always rising and dropping. Other countries that have access to tidal energy are Scotland and South Korea. Between 2002 and 2003 Scotland founded the biggest tidal energy project in Europe. Between 2003 and 2010 the Sihwa Lake tidal project in South Korea was built. United Kingdom and Canada have also installed tidal power projects into their countries.
What variations and different models of Tidal energy machines exist?
There are many different styles of turbine machines that are used for tidal energy. I will be explaining the 3 tidal generators used, their model structure and how they are unique and different from each other.
Tidal streams:
Turbines are usually placed in tidal streams. Tides create quick flowing of water which is a tidal stream. Turbines are created to transfer the energy from the body of water and turn it into natural power. Turbines are best when placed in shallow waters and this allows the turbine to move more affectedly and power more energy. Ships can avoid these turbines in low waters and the tidal turbine moves slowly so animals can keep away from getting harmed.
Tidal barrages:
Tidal barrages are placed in bays, estuaries and tidal rivers. This design of the barrage allows water to come through the top or travel through the turbines in the dam since the dam is shallow. The opening of the barrage closes and opens depending on tide height. If the tide is high the barrage gate shuts and allows the water to turn into a pool; once the tide is low the barrage gate closes allowing water to come through. Once the water comes through the barrage it is released into the barrages turbine and then turns into energy and power. Overall the energy from the tides makes the turbine spin and compresses the air to form electricity. Tidal barrages are built with materials including ridges, turbines, heavy ship locks and are stored in huge concrete blocks.
Tidal lagoons:
Tidal lagoons are similar to Tidal barrages and complete the same water turbine process however there are some differences. Tidal lagoons are placed along coastlines and they are constantly making energy. The lagoon is repeatedly and filling and emptying and the tidal energy machine work to make power in that area of water. These Tidal lagoons are built with materials such as hard rocks and cement.
This is the website that I accessed this video from
https://www.studentenergy.org/topics/tidal-power
MLA citation website:
Kabeya, Annick. Tidal energy, Student energy. Accessed 6 Nov 2019. https://www.studentenergy.org/topics/tidal-power.
What are the pro’s and con’s of tidal energy?
PRO’s:
Tidal energy is a renewable energy source and it is natural and friendly to the ecosystem. It doesn’t take up massive space and doesn’t release any toxic or harmful gases into the environment. The ranges of the tide are also dependable and exist daily. The tidal energy machines are capable of handling high and low tides and the equipment is durable and strong. Aside from this; tidal energy is also efficient and can produce energy at low tides. This is because water has 1000 times more density than air which makes it possible for it produce this energy. The tidal power station that opened in 1966 in France is still powering and creating renewable energy. This is an example of how tidal energy machines can last a long time and can create large amounts of energy.
CONS:
Although tidal energy can be very resourceful and helpful to energy production and the environment; there are some concerns and issues with this form of energy. Tidal energy machines are placed closed to land and this can interfere with machinery, and technological working areas. Tidal energy is also very expensive to implant as it is a new form of energy and technology. Electromagnetic release can also be irritating to sea life. There was an observation of how this discharge can harm the ability for Coho salmon to find food and avoid predators. Although there needs to be more advanced research for the relationship between animals and electromagnetic emissions, there are some evidence of negative impacts with sea life.
This is an image of the ocean tide
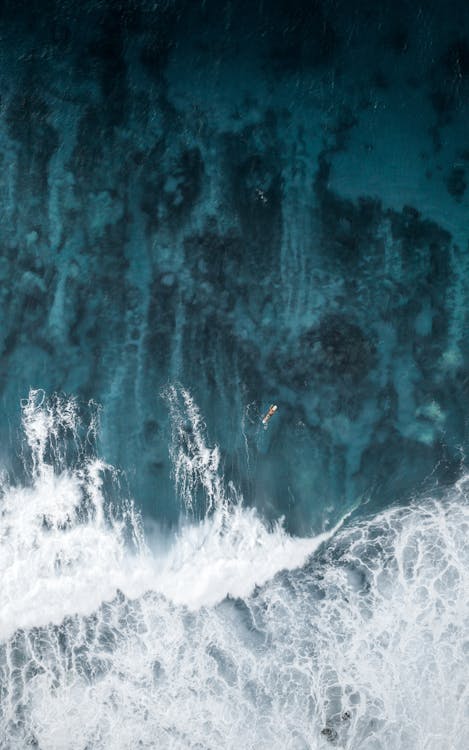

I accessed this image from the website ”Pexels”
Tidal energy compared to wave energy?
Wave energy:
Wave power is the movement of energy through the waves and flow of the ocean. The pull of kinetic force allows waves energy to generate power. The wave energy machines contain objects that will move and shake in the water. This movement will create a small amount of energy to the machine causing wave energy. The machines used for creating wave energy are buoys floating in the ocean. Swaying water columns and water channels are also used in useful ways to generate energy. Wave energy is a renewable energy source; and waves along with rising tides are dependable and predictable to occur. Wave energy has generates a large amount of power. A wave area that is measured to be around less than half a square mile of the ocean can create enough energy for 20,000 houses. Although wave energy can have many positive benefits there are some concerns with this energy source. Wave energy is a new type of technology so it is very expensive and requires money from the government to make it function. Wave energy also requires regular supporting and maintenance. Another concern is that wave energy areas on the shore, near shore or on land can cause some issues with development, building and people in that area. There also needs to be more information and advanced research about its impacts underwater, effects with animals and other issues.
This is an image of a Tidal energy machine located in the ocean
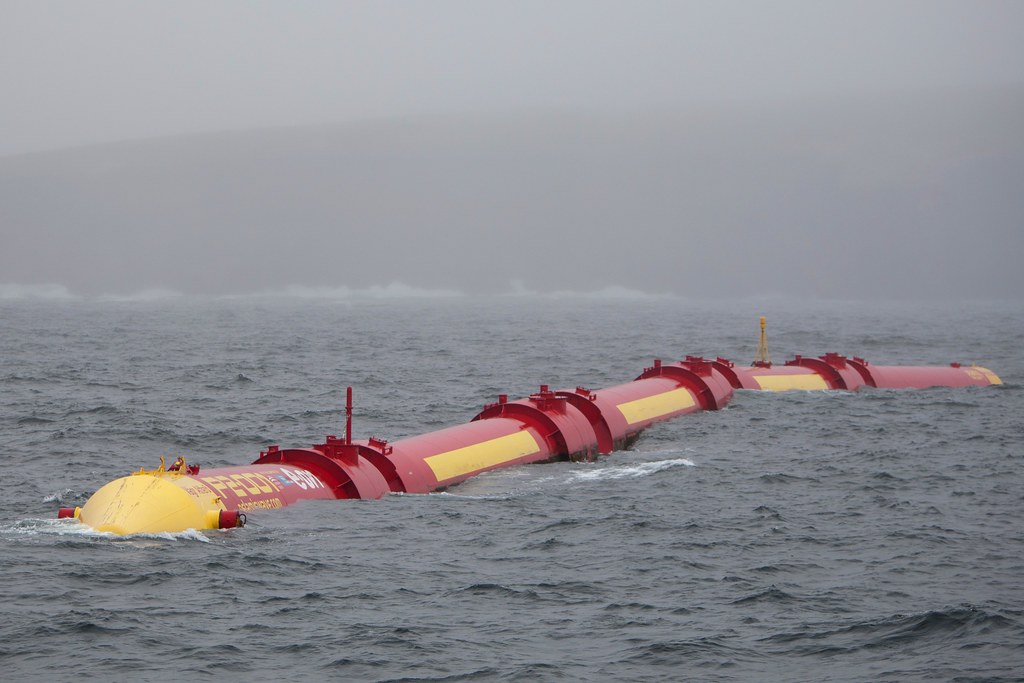

“Pelamis P2 wave energy device” by Scottish Government is licensed under CC BY-NC 2.0
Tidal vs Wave energy:
These two energies are very similar to each other as they both involve machines that generate energy from water sources. They also have similar pro’s and cons. The cons are that they are both costly, and involve the same concerns, and issues. The pro’s are that they are both renewable, clean and are new technologies of energy. They both generate a large amount of energy and have different variety’s of machines. There are some differences such as tidal energy uses the gravitational pull from the earth to power energy while wave energy uses kinetic energy. Tidal energy machines are also located on coastlines and have many energy machines used in different locations. Wave energy machines are located in the water, on shore, offshore and near shore. Overall these energies are very resourceful and involve a deeper extent of research to improve their functioning.
Analyze:
My statement to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau:
After researching my questions about Tidal energy I have become more educated on this topic and think that Tidal energy is a great renewable source. North America’s only functioning Tidal energy plant is located at Annapolis, Nova Scotia.It produces 80-100 megawatts of electricity annually for Nova Scotia’s electrical system. Tidal energy is a long-lasting, efficent, clean and generates a lot of electricity. Using this source of power can help generate electricity in so many homes and reduce the amount of greenhouse emissions. There are many estuaries along the coast of British Columbia that can be used for tidal energy. The Ungava Bay in Northeastern Canada has fairly high tides. There are also more areas with higher tides than waves. Compared to wave energy, tidal energy doesn’t involve constant maintenance as it is self-sufficient. Tidal energy is cautious of marine life and the slow turning turbines don’t disrupt or harm wildlife. Our country can weigh out the statistics and find out which areas don’t have access to electricity, and have the proper space and area to implant these machines. Tidal energy is also free from loud noise and doesn’t disrupt people or buildings. The biggest concern with Tidal energy is it’s cost and the funding from the government. I think that there does need to be more research done with Tidal energy and Canada can promote Tidal energy to their country to get others more educated. We can also fund money for Tidal energy research organizations and discuss the future of Tidal energy in our country. Canada is known for it’s effort towards creating a healthy, and clean ecosystem. Using this type of energy can lead to more renewable oppurtunties and can get other’s involved and interested in Eco-friendly energies. Although tidal energy is a newer technology and needs further research I think it should be deeply discussed by the government and we can take small actions to fund for Tidal energy and use our energy in a reusable way. The Tidal energy plants in France are a great success and have helped the country in so many positive ways. Canada should take insight of other country’s actions towards tidal energy and renewable sources. The future of a green earth is renewable tidal energy.

I accessed this photo from the website ”Pexels” “FLOWLIGHT – Renewable Energy Product” by Shane Molloy is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
Assess:
I worked very hard on this project and followed all the steps to complete the Information fluency method. I chose a topic I was interested and passionate about and learned so much new information about Tidal energy. I learned the process of it, the issues and positive effects, the different machines, and compared it to other energy sources. I was very interested in learning about how renewable energy sources can make a great impact in our lives and all over the world. I developed detailed questions of my topic before starting my research. I focused on branching out onto different websites and finding accurate and true data. I found my images on Pexels and Creative Commons and used Youtube, Google and Gale to find my research. I examined each website critically and used multiple websites to match my information. I also developed new skills of reading about the author, illustrator and understanding the websites motive and value. I cited all my work in the MLA format and organized my research in a neat matter. I also got to take my knowledge and findings and create my own opinion and response about my view of Tidal energy. I am proud of the detail, time, and effort I put into this project. Reflecting back on my process there are some improvements I could have made. I could have added more detailed questions that are specific to Canada and it’s use of Tidal energy. I also could have made my research more detailed and interesting. I also could have spent more time finding websites that I haven’t used and branch out from my comfort zone. Overall I am pleased with my work and excited to learn more about Tidal energy and other renewable sources that can benefit Canada.
Other sources and websites used (MLA format):
Alcorn, Raymond. Wave energy, Science direct, Accessed 8 Nov 2019. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/wave-power.
Wave energy Pro’s and Cons, energy informative, Accessed 8 Nov 2019. https://energyinformative.org/wave-energy-pros-and-cons/.
Tidal energy, National Geographic, Accessed 6 Nov 2019. https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/tidal-energy/.
“Riding the waves.” Earth Island Journal, Winter 2014, p. 6+. Gale In Context: Science, Accessed 9 Dec 2019. https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A353319114/GPS?u=43sbo&sid=GPS&xid=3146830e.
R.H, Clark. Tidal Energy, The Canadian Encyclopedia, Accessed 8 Nov 2019. https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/tidal-energy.

I accessed these image from the website ”Pexels”
