A biofuel is a fuel that comes from a living or recently dead organism and can be in the form of liquid, solid or gas. Biofuels are used to power cars, heat homes, cook, as well as many other things. A biofuel is not a fossil fuel – a fossil fuel is a fuel that comes from long-dead organisms. Biofuel is a kind of renewable energy, energy generated from natural resources like sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat. This type of energy is naturally replaced or replenished.
There are many biofuel companies in Europe, Asia, and the Americas. One company in the United States found that even pollution can be converted into renewable biofuel.

http://cee.illinois.edu/news/optimizing-location-biofuel-production-plants
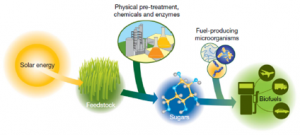
One of the common types of biofuels are agrofuels. Agrofuels are produced from specific plants, for example, to make ethanol, corps that are high in sugar and starch are grown. Vegetable oil from plants can be used as a biodiesel, this oil is heated and burnt directly in a diesel engine. Wood can be transformed into biofuels as well, like charcoal, methanol or ethanol fuel. Also, wood and grasses can be dried, put into pellets, and then burnt to get power.
https://blogs.biochem.ncsu.edu/biofuels/
The greatest advancement in using biofuels is that we are able to use almost anything, like corn, or sugar, for example, and turn it into energy. Biofuels are becoming less and less expensive, as well as getting to be easier to produce, which is helping to replace other fuels. Even though, biofuels cannot be produced in large portions and are usually mixed with other kinds of fuels to be more effective. Sometimes, a biofuel on its own does not even give the amount of energy that was used to produce it! Although, biofuels are much better for the environment than, for example, petroleum.
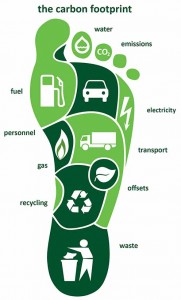
While biofuels have many advantages, like their decreasing prices and how easy they are to source, this type of fuel also has many disadvantages. As mentioned above, even though the carbon footprint of biofuels is less than that of other fuels, the process with which they are produced is worse for the environment, making up for the environment-friendliness of the biofuels themselves. Usually, the process includes the use of large quantities of water and oil, and big industries meant for churning out biofuel often cause water pollution and emissions.
http://beagreencommuter.com/how-to-calculate-your-carbon-footprint/

Bibliography:
“Biofuel.” Wikipedia. n.d. Web. 9 Nov. 2016.
Energy 101 | Biofuels. U.S. Department of Energy, 19 July 2012. Web. 9 Nov. 2016.
Biofuels, the Green Alternative. AFP News Agency, 7 Feb. 2012. Web. 9 Nov. 2016.
Daniel Ciolkosz, P. E.,”What Is Renewable Energy? (Renewable and Alternative Energy).” Penn State Extension. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Nov. 2016.
National Geographic Society. “Biofuel Facts, Biofuel Information.” National Geographic. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2016.
“6 New Things Happening with Biofuels.” Energy.gov. N.p., 19 June 2015. Web. 11 Nov. 2016.
“Advantages and Disadvantages of Biofuels.” Conserve Energy Future. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2016.
“Time for Change.” What Is a Carbon Footprint. N.p., n.d. Web. 12 Nov. 2016.






