Causes of the American Revolution
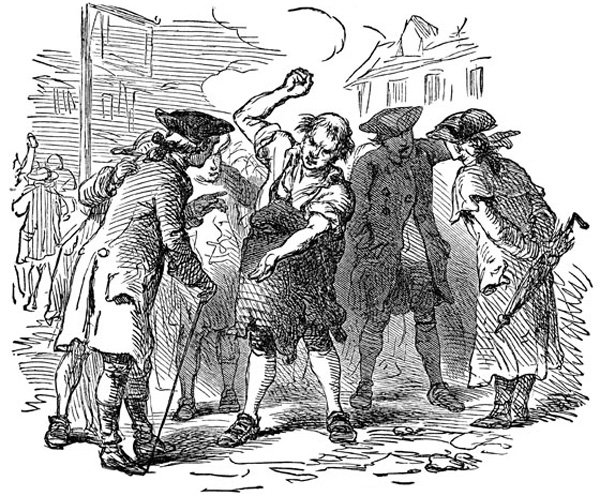

Stamp Act: The Stamp Act Denounced
http://ushistoryimages.com/stamp-act.shtm
The Stamp Act was introduced to pay for the cost of the French and Indian war. It was the first direct tax on the American colonies. Newspapers, pamphlets, bills, legal documents, almanacs, dice and playing cards were taxed. The colonists were infuriated because they felt they should be taxed only by their own government. The Sons of Liberty formed to oppose the Stamp Act and used violence and intimidation to fight against it. Samuel Adams lead the group in Boston. October 1765 representatives from nine colonies met in New York and sent a petition to King George and Parliament asking for the Stamp Act to be repealed. The petition stated taxation without representation violated their basic rights. The colonist refused to use the stamps when the Stamp Act went into effect November 7 1765.
In June, 1767 the British Parliament decided to cut British land taxes, however they needed to fund a war in France and India. To make the difference, Charles Townshend promised to tax the colonists on all their imported goods. The colonists were angry about that. In October the colonists decided to boycott most imported English items. In February Samuel Adams wrote a letter to Parliament, complaining, and it later became known as the circular, and told the colonists to rise up against England. After many meetings and disputes, England sent in warships to the Boston harbour. People complained about being taxed without representation, and after a lengthily dispute the Townshend act was repealed, except for the taxes on tea.
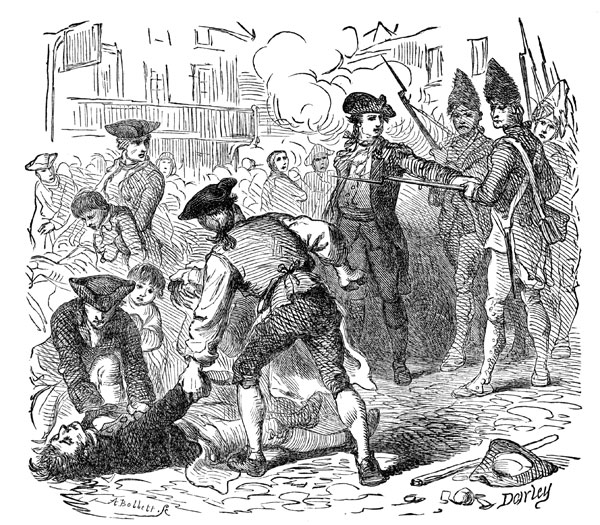

Boston Massacre: The Boston Massacre
http://ushistoryimages.com/boston-massacre.shtm
In February 1770 Christopher Sneider, a young colonist boy, was killed by a British merchant, and put the colonists and soldiers at edge with each other. On Monday, March 5th, 1770 a conflict grew between the colonists and British soldier, and the colonists started throwing snowballs and rocks at them. Private High Montgomery was hit by a club, and started firing intot he crown, making other people fire as well. Three colonists died there, two died later from injuries they sustained. Sam Addams insisted the troops leave Boston, and many who were for the independent from British blew the fight out of proportion, thus naming it the Boston Massacre.

Boston Tea Party: Destruction of Tea
http://ushistoryimages.com/boston-tea-party.shtm
In 1773 the East India Company had plenty of tea that it couldn’t sell, so the British government gave it special permission to sell its tea in the colonies without tax, making the Tea Act. The British government didn’t think that the colonists would be upset about this, but they were. It would give the East India Company a monopoly on tea sales. The colonists decided to restart the boycott on English tea, and got even more people joining it; women, the primary drinkers of tea, joined in. The colonies decided to stop the East India Company from selling tea in America. In October 1773 Philadelphia opposed the tax and forced British tea agents to leave their positions. On December 16th 1773 Samuel Addams lead three groups of 50 men, dressed as Mohawk Indians, and broke into 342 chests of tea, and threw all the tea overboard. After the damage was done, the colonists refused to pay for the damage they made.

Patriot cartoon depicting the Coercive Acts as the forcing of tea on an American woman
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intolerable_Acts
The Intolerable Acts were passed in 1774, and they did not allow British soldiers to be tried for any crime they may commit in America, nor did they let them get tried in England, meaning they could do whatever they pleased. There were three major events that angered the colonists. On June 1st, 1774 the Boston Port Bill was passed, and it closed the Boston harbour until the colonists paid for all the tea they destroyed.
On September 5th 1774, every colony, except Georgia sent representatives to what would later be known as the First Continental Congress. There were 44 delegates present. On October 26th 1774 congress adjourned and decided to meet again in May, of 1775 if King George III did not repeal the Intolerable Acts. King George III refused to remove the acts.
—
Components

Battle of Lexington, april 1th, 1775
http://ushistoryimages.com/battle-of-lexington.shtm
King George III told General Thomas Gage to use force to ensure that the colonies knew that the British still ruled. This put the British and the colonists even more at edge with each other, and that made the colonists even more convinced to bear arms. The colonists who were for the independence of America were called patriots, but in Massachusetts were known as Minutemen, as they were ready at a minute’s notice. During April in 1775, General Gage learned that Patriots had an arsenal of weapons, stored in the town of Concorde, and he ordered his soldiers to go there and capture the weapons. On the way there, they decided to go through Lexington to look for Samuel Adams whom they wanted to arrest. The Minutemen, Patriots, had learned that the British were coming, somehow, and went to Lexington and waited for the British to come. In the morning of April 19th, the British marched through Lexington and were met by seventy Minute men. The British fired two volleys, eighteen minute men were killed, but the rest scattered. The British went on to Concord where they did not find the weapons they were looking for. While the British soldiers were making their way back to Boston they were shot at by Minutemen. The soldiers were stuck between the sea and the rag tag Patriot army. In the end seventy three British soldiers were killed, and two hundred forty seven were wounded or went missing. The Patriots only lost ninety three. General Gage decided until he could get reinforcements, he would not use anymore force against the colonists. Though not many people realized, that was the beginning of the civil war.
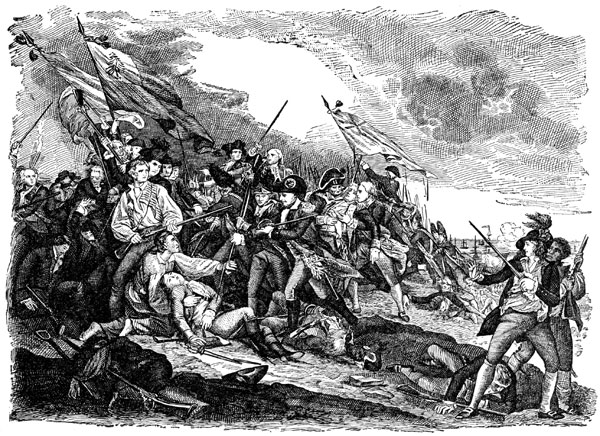

Battle of Bunker Hill – June n17th, 1775
http://ushistoryimages.com/battle-of-bunker-hill.shtm
The battle of Bunker Hill was the first major battle of the American revolutionary war. General Howe was the leader of the British army, which still had a strong presence in Boston, which upset the Patriots. By taking over Dorchester Heights and the Charleston’s peninsulas, the British knew they would watch over the Boston harbour. The Patriots found out about the British’s plan and decided to act. On the June 17th, 1775, the British troops found the Patriots had taken control of Bunker Hill. They began to attack from the sea, but later moved to make an assault on the ground. Twice the British retreated; the Patriot’s fired at them as the British approached, but where sent back to fight. On the third try the British were more successful. The Patriots had run out of gun powder and were forced retreat. Even though they lost, the Americans realized that it took the British three tries to win, and that gave them confidence to fight again.
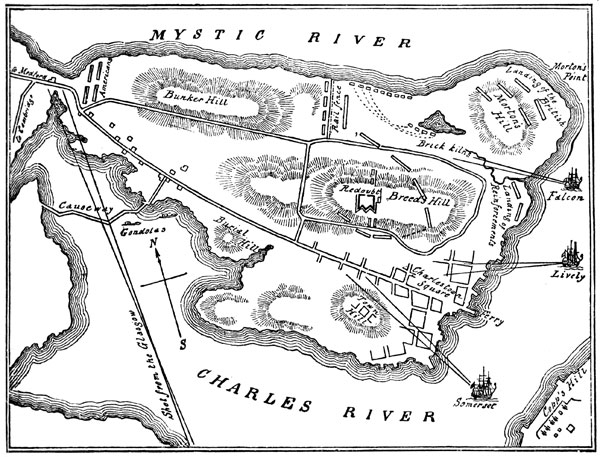
Plan for Bunker Hill
http://ushistoryimages.com/bunker-hill.shtm
Thomas Paine wrote Common Sense in January, 1776, a pamphlet that described what was happening in the colonies because of the British, how it was unfair and why America should declare independence from its mother country. It wasn’t publish until February 14th of the same year. Within months of its release more than 500,000 copies had been sold. Common sense convinced many people that what the British were doing was wrong, and the only way to protect their rights was to declare independence, and gave people a desire to fight for their freedom.
On May 5th of 1775 the Second Continental Congress met in Philadelphia. The Patriots wanted to try and work things out in more civil fashion, and offered The Olive Branch Petition to try and avoid a war. King George III refused to read it. Most American’s agreed that there was no choice but to declare independence. There was quite a bit of frustration from the Patriots, who did not want independence at the cost of war, but on June 7th, 1776, Richard Henry Lee made a formal proposal that that the colonies declare independence. Congress appointed a five man committee to write a declaration of independence, led by Thomas Jefferson. It took two weeks for Jefferson to finish the declaration, and it was presented to congress and debated on July 1st. After going over it many time, the declaration has taken its final form on July 4th.
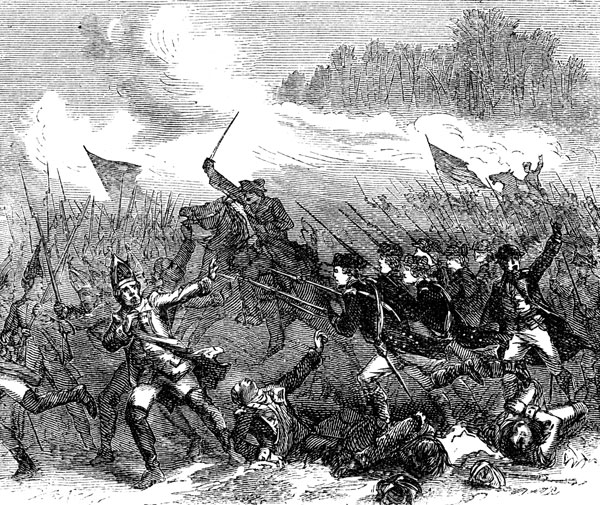

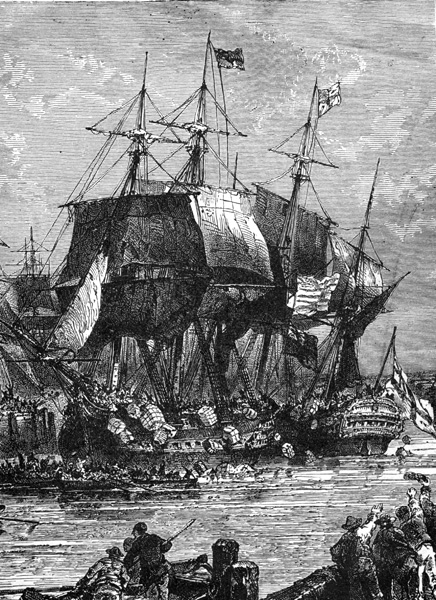
SURPRISE OF THE HESSIANS AT TRENTON
http://ushistoryimages.com/battle-of-trenton.shtm
During battles the Patriots has suffered many losses, and after the battle of New York General Washington’s army fled to Pennsylvania’s country side to get away from the British troops. On Christmas night of 1776, General Washington made a plan that he thought would bring victory to his men. He guessed that the Hessians, the German army, would be celebrating Christmas and wouldn’t expect an army strike. The group of soldier crossed the Delaware River where they were camped out in boats, when they all reached the other side in the early morning, they used surprise as their weapon, and captured between 900 and 1000 prisoners and took over Trenton. They went on to Princeton and again surprised their enemy.

British general John Burgoyne earned the nickname “Gentleman Johnny” for his love of leisure and his tendency to throw parties between battles. His surrender to American forces at the Battle of Saratoga marked a turning point in the Revolutionary War.
http://www.ushistory.org/us/11g.asp
In September, Major General Burgoyne and his men reached Albany, only to find it protected by 7,000 Patriots following the orders of Major General Horatio Gates. On the 19th of September, 1777 the British attacked the Patriots, and forced the Patriots to retreat to Bemis Heights. The battle restarted on October 7th, when the British staged a full assault on the Patriots at Bemis Heights. The Patriots had let he British wear themselves down with minor assaults and were prepared on October 7th. They had a strong defense up against Burgoyne’s army. The British had no choice but to retreat. On October 17th, 1777 the British army had no choice but to surrender to the Patriot army. That battle ruined the goal of British control over the Northern colonies. The French had also decided to join the Patriots against the British army, and that, along with the gained control of the Northern colonies gave the patriots reason to continue fighting.

Detail of a 1780 map drawn by a British engineer showing the Charleston defenses
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siege_of_Charleston
After the battle of Saratoga General Sir Henry Clinton focused on the southern colonies and decided that the best course of action was to send troops there. Lieutenant Colonel Campbell captured Savannah, Georgia in December of 1778. On January 19th, 1779 Brigadier General Prevost took control of Augusta, giving the British full control of the Georgia colony. Then on May of 1789 the British recaptured Charleston, after forcing General Lincoln’s men to surrender, making amends to their loss in June, 1776. In order to reinforce General Charles Lincoln’s troops, General Washington sent unit of men from Maryland and Delaware to aid them. Soon after they were ordered to march into Camden by General Gates. On August 16th of 1780, the British army battled the Continental forces in South Carolina. When the Patriot army saw they were outnumbered they retreated, giving the British control of yet another major city in the Carolinas. General Gates was soon replaced by General Greene after that defeat. The Patriots won the battle o0f Kings Mountain on October 7th, 1780 when the British leader, Patrick Ferguson was killed and his troops surrendered. Three months following on January 7th 1781 General Greene defeated General Cornwallis’s troops, giving them the victory of the Battle of Cowpens. On March 15th of 1781 the British won the battle at Guilford Courthouse, even though they were forced to retreat. General Greene and his troops remained in South Carolina and worked with Vigilante groups to push the British out. They were defeated by the British at Hobirks Hill on April 15th, 1781, and again at Eutaw Springs on September 8th 1781. Despite the British’s victories they were worn out and retreated to Charleston, setting the stage for the final battle in the American revolutionary war.
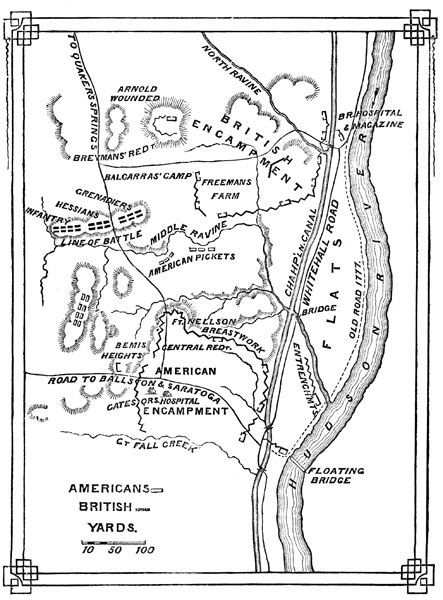
PLAN OF THE BATTLES OF STILLWATER AND SARATOGA
http://ushistoryimages.com/battle-of-saratoga.shtm
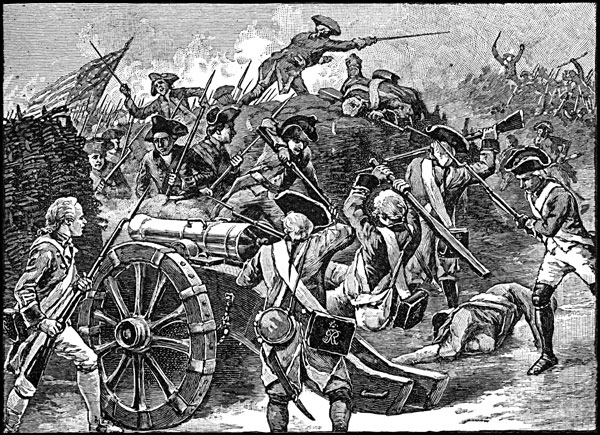

CAPTURE OF REDOUBT AT YORKTOWN
http://ushistoryimages.com/battle-of-yorktown.shtm
After the battle of Guilford Court House the British were tired and worn out, and General Cornwallis decided to move his troops to Yorktown, Virginia. At the same time, General Washington was planning to attack New York, and General Cornwallis was ordered to move all his troops to New York however he did not obey orders. On October 6th 1781 the Continental army, with the help of the French, attacked General Cornwallis and his men in Yorktown. A British fleet was sent from New York to aid General Cornwallis but it was too late. On October 19th, 1781, General Cornwallis and his men officially surrendered to General Washington. No one realized at the time but this was the last major battle of the war. In April of the following year the British House of Commons voted to end the war.
The British were forced to surrender 2 days after patriot soldiers captured the fort at Yorktown in 1781
Consequences
After the American revolution ended, most Loyalists – colonists were where loyal to the crown – went to other British colonies, such as Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. There were so many Loyalists in one place, that they created Ontario.

treaty of paris 1783
http://www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/treaty-of-paris
The Treaty of Paris of 1783, ended the revolutionary war, and made Great Britain recognized the United States as an independent country. They established the ground that was considered American, and English. Britain allowed the United States the Allegheny Mountains to the Mississippi river, giving the United States its new borders.

Page one of the original copy of the Constitution
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States_Constitution
In 1789 the United States created the Constitution, the “Supreme laws of the land” and ventral instrument of government. The Constitution states that there are three main branches of government, and three levels of government, and that no branch of government is more powerful than any other. No person is outside of the law, and in all states they must be democratic and respect the laws of each other.

Amendment 10: “The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.”
http://www.ushistory.org/us/18a.asp
There were ten first amendments to the Constitution, and they became known as the Bill of Rights, established in 1791. The Bill of Rights represents the ideals that the United States valued then, and still now; personal liberty, limited government and the rules of law. The Bill of Rights state that every individual has personal rights, such as the right of freedom of speech and right to petition the government. Even today people have these rights and more.
The American revolution put the idea and prospect of person rights and equality into the heads of other people around the world. Suddenly, the idea that saying no to a person or government that was in power, and using it poorly wasn’t as daunting as it was before. The American revolution set the stage for other revolution around the world.






































![http://www.uppercanadahistory.ca/wm/wm9.html Fanciful version of the Death of Montcalm by François-Louis-Joseph Watteau {The original is in the National Gallery of Canada} [Inspired by West's Painting of the Death of Wolfe]](https://myriverside.sd43.bc.ca/jessicak-2014/files/2015/01/wm9p10d-z53yat-300x218.jpg)
























