Biofuel: Harry & Diana
Introduction
Many scientists have been trying to discover a way to find natural and renewable alternatives to replace traditional fuels such as gasoline and diesel, their goal being to help the environment by decreasing (if not fully stopping) greenhouse gas production and reducing the world’s reliance on fossil energy sources. The idea of Biofuels is the study and process of using natural and renewable resources and creating them into fuels to power the engines of transportation vehicles. Not only can these biofuels be used for transportation, but also for power generation and heat by burning biomass materials. The advantages of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels are many and unambiguous, but there are incredulous people who think biofuel is not trustworthy because with so many advantages, it is rare to not have some downfalls. Biofuels have a lower energy output than traditional fuels, meaning it is required to create a much greater quantity to produce the same energy as other fuels. Needing more resources means that the demand for certain crops will rise, resulting in a rise of their prices at the market and shortage of water.
What are the greatest advancements in regard to Biofuels?
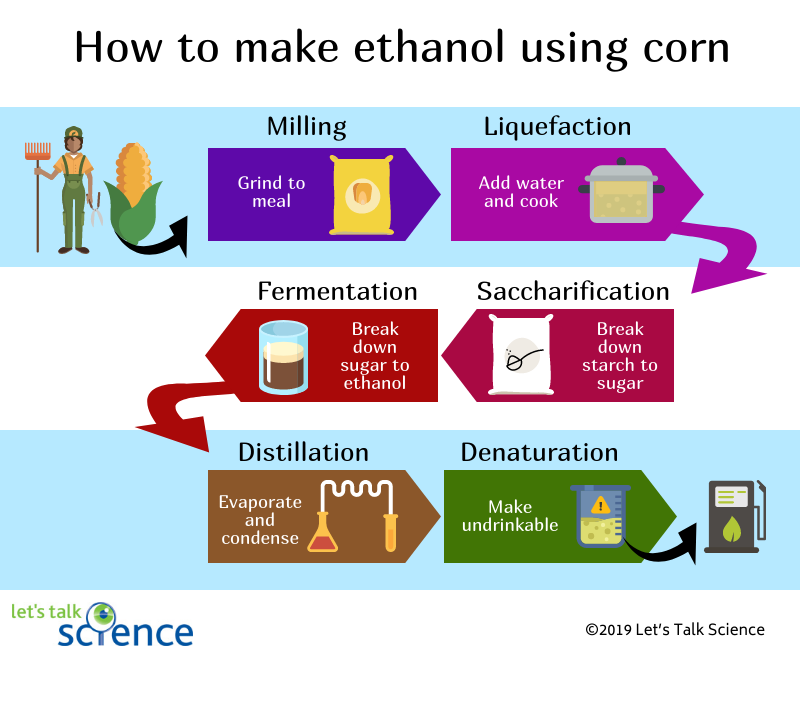
During the late 1890’s, a German mechanical engineer Rudolf Diesel created the well-known Diesel engine, and a few years later in 1900, Diesel was able to present his creation by running it on peanut oil. Other creations followed such as the invention of the Model T Car by Henry Ford in 1920’s which ran only on biofuels, as well as the creation of gasoline in 1920. But the invention that changed most of history was the creation of Ethanol during WWI and its extensive use during 1910s – 1940s. It was majorly used due to the shortages of fossil oil and the limited imports of oils because of the wars. Ethanol is a clear, colourless, alcohol made from sources such as starches, sugars, and vegetable oils that come from breaking down corn and wheat. The process is difficult in itself – milling your input materials (also known as feedstock), the liquifying the mixture before breaking down the starch and sugar into ethanol. Corn ethanol has two main by-products: carbon dioxide and distillers’ grains, in other words, the residue from the fermentation tanks. Even though there are many citizens who prefer using ethanol, there are some that worry about the amount of energy and land that is required to grow crops used for ethanol. These concerns are valid, but considering the advantages of using ethanol, it is still better than fossil fuel usage.
How are Biofuels best used?
Biofuel is one of the greatest innovations in biotechnology, and it is best used as an alternative to fossil fuels because it provides more renewable energy and reduces pollutant than fossil fuels. Biofuel is a renewable energy produced from biomass materials such as plant, algae, or animal waste. Unlike fossil fuels, biofuel is a source of renewable energy because these feedstock materials can be replenished indefinitely. While fossil fuels are more proficient for the use of vehicles, biofuels are more efficient for generating usable energy. For example, biodiesel, a type of biofuel derived from animal fats and vegetable oils, provides 93 per cent more energy than fossil energy. Biofuel also emits less carbon emission than fossil fuels. Ethanol, a main production of liquid biofuel, contributes approximately 85 per cent less carbon emissions into the atmosphere than gasoline. Ethanol is often blended with petroleum-based diesel and gasoline because of the benefits it provides to our environment. The government of India has established a goal to achieve 10 per cent ethanol-blending in gasoline by 2022, and 20 per cent by 2023. This progress will gradually minimize the dependence on fossil fuels as the percentage rises. Governments and automobile industries have recognized the efficiency of biofuels, and they are working towards to bring it to everyday use in our society. Thus, embracing biofuel will significantly benefit our economy. Biofuel demand is rapidly increasing at a rate ten times faster than that of fossil fuels.

How are Biofuels changing the world as we continue to advance?
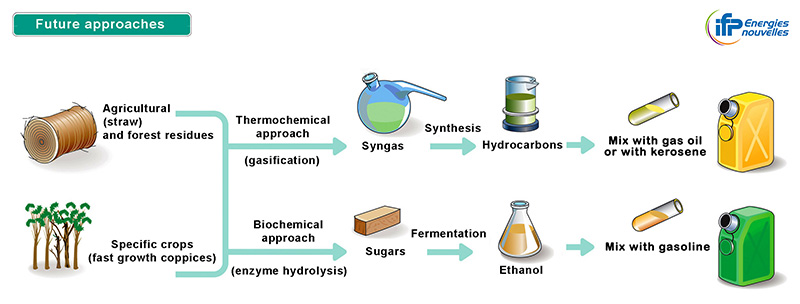
Biofuel has a high expectation to change the world in the future. It is still ambiguous if biofuel is changing the world today because we only use little, but the changes will be noticeable if we completely replace fossil fuel with it. Future role of the biofuel will mostly depend on profitability. Due to volatile price of biomass materials, biofuel profitability will be variable. If there are enough profitability and technologies to support biofuel, it will benefit the world economically and ecologically. First, it is changing the world economically by enhancing energy security. Energy security refers to an access to sustainable and affordable sources of energy. Countries with surplus energy are secured in energy while countries with energy deficiency are not secured in energy. Many countries pursue energy security because it can be a breakthrough for their economy. Next, it is changing the world ecologically. Current studies are focusing on using fuels with higher percentages of ethanol blends. Higher percentages will allow the engines to combust the fuel more completely, which will mitigate carbon emissions in the atmosphere.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biofuel has a lot of potential for future growth of the world because it is a renewable alternative to replace traditional fossil fuels, an effective method to reduce carbon emissions, and eco-friendly energy resource that can significantly benefit the economy. It will be another huge biotech innovation if it completely replaces fossil fuels. Upcoming revolution of biofuel will eventually reduce consumption of fossil fuels and present new biotechnology to us.
Works Cited:
“Biofuels in the EU: A Vision for 2030 and Beyond.” Biofuels, 10 July 2021, www.biofuelstp.eu/.
Chen, James. “Biofuel Definition.” Investopedia, 19 May 2021, www.investopedia.com/terms/b/biofuel.asp.
Hill, Jason, et al. “Environmental, Economic, and Energetic Costs and Benefits of Biodiesel and Ethanol Biofuels.” PNAS, 2 June 2021, www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0604600103.
“History of Biodiesel Fuel.” Pacific Biodiesel, 12 Jan. 2020, www.biodiesel.com/history-of-biodiesel-fuel/.
Hoyle, Brian Douglas. “Ethanol.” Gale, 24 November 2021, https://go.gale.com/ps/retrieve.do?tabID=T001&resultListType=RESULT_LIST&searchResultsType=SingleTab&hitCount=252&searchType=BasicSearchForm¤tPosition=1&docId=GALE%7CMXMPIZ951121537&docType=Topic+overview&sort=Relevance&contentSegment=ZXAS-MOD1&prodId=GPS&pageNum=1&contentSet=GALE%7CMXMPIZ951121537&searchId=R3&userGroupName=43riss&inPS=true
“India Brings Forward Target of 20 Percent Ethanol-Blending in Petrol to 2023.” The Economic Times, 2 June 2021, economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/energy/oil-gas/india-brings-forward-target-of-20-percent-ethanol-blending-in-petrol-to-2023/articleshow/83180631.cms?from=mdr.
Levac, Krysta. “How Is Ethanol Made?” Let’s Talk Science, 13 Aug. 2018, letstalkscience.ca/educational-resources/backgrounders/how-ethanol-made.
“Liquid Biofuels for Transport Prospects, Risks and Opportunities.” Biofuels: 1. What Are Biofuels?, www.greenfacts.org/en/biofuels/l-2/1-definition.htm.
Nagel, Miriam C, et al. “Biofuels.” Gale, 2021, https://go.gale.com/ps/retrieve.do?tabID=T001&resultListType=RESULT_LIST&searchResultsType=SingleTab&hitCount=498&searchType=BasicSearchForm¤tPosition=4&docId=GALE%7CCX8124400319&docType=Topic+overview&sort=Relevance&contentSegment=ZXAR-VRL&prodId=GPS&pageNum=1&contentSet=GALE%7CCX8124400319&searchId=R1&userGroupName=43riss&inPS=true
“New Developments: Scientists Build Bioreactors and Engineer Bacteria to Advance Biofuel Research.” Gale, 28 February 2022, https://go.gale.com/ps/retrieve.do?tabID=T003&resultListType=RESULT_LIST&searchResultsType=SingleTab&hitCount=3327&searchType=BasicSearchForm¤tPosition=1&docId=GALE%7CA696022782&docType=Brief+article&sort=Relevance&contentSegment=ZXBE-MOD1&prodId=GPS&pageNum=1&contentSet=GALE%7CA696022782&searchId=R1&userGroupName=43riss&inPS=true
“4 Reasons Why the World Needs Biofuels.” Neste Worldwide, 28 Sept. 2016, www.neste.com/4-reasons-why-world-needs-biofuels.
“What Future for Biofuels?” IFPEN, 1 Mar. 2020, www.ifpenergiesnouvelles.com/issues-and-foresight/decoding-keys/renewable-energies/what-future-biofuels.
Zhang, Siruo. “Biofuels.” Biofuels, 2015, allaboutbiofuels.wixsite.com/biofuels.
Core Competency:

