Biomes in each region.
- Cordillera: Coast and Interior Forest, Grassland, Tundra, Coniferous forest, mixed forest, parkland.
- Interior Plains: Mixed forest, grassland, coniferous forest, tundra
- Canadian Shield region: Subarctic, tundra, mixed forest, coniferous forest.
- Arctic region: Tundra, subarctic.
- Lawrence Lowlands: mixed forest
- Appalachian: Coniferous forest, mixed forest.
Mount Waddington (B.C) for Cordillera region because: shows its abstract peaks and mountain range. Shows glaciers and ice fields. Created by plate collision, pushing and folding mountains along with erosion.

Waterton Plains Alberta for Interior Plains because: shows the vast area of grassland yet with rolling hills and even though the plains are dry it shows some of the coniferous and mixed forest. Created from soils carried from the shield in rivers to layer upon one another.


Lake; Ontario for Canadian Shield because: shows it as flat bare rock and surrounded by water as erosion and weathering has brought it down to. not very populated. Weathering caused the once volcanic mountain range to diminish to flat areas.
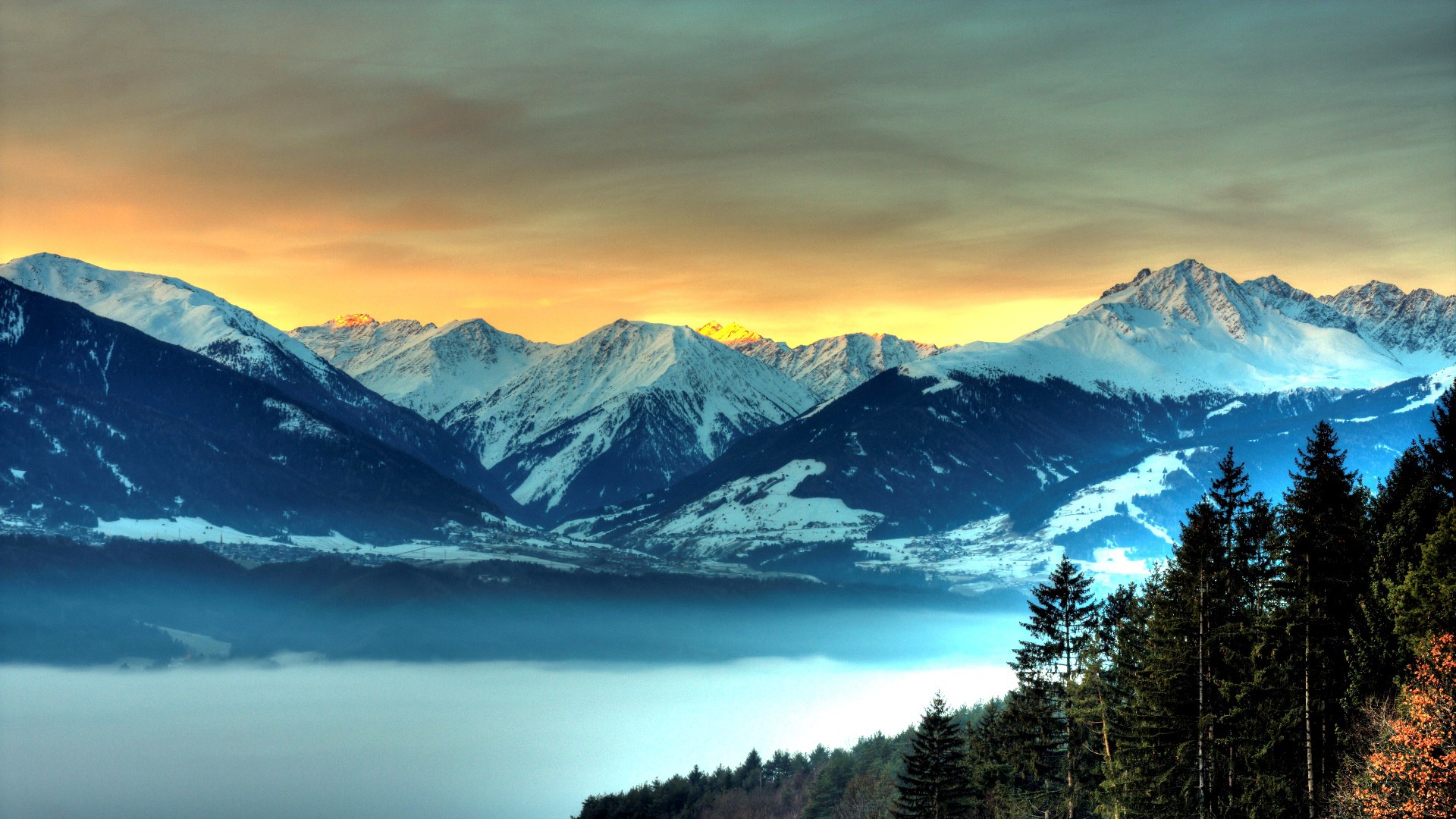


Innuitian Mountain for Arctic region because: good example of fold mountains. Composed of sedimentary rock and covered in snow. The shield pushed rock thus forming the fold mountains.


St. Lawrence River for St. Lawrence lowlands because: very green flat fertile soil. Patches of orchards an farming with water source. When ice melted and then grew and froze once more it pushed the soil underneath causing the lowlands.


Appalachian Mountain region: shows the fjord and mineral deposits. Mountain and highlands. Sedimentary rock. Made by weathering and erosion of mountain ranges and glaciers.


Leave a comment