Eubacteria
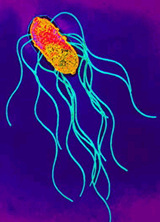
1) Salmonella Enterica
Rod Shaped, Gram-Negative bacteria, species of the genus Salmonella.
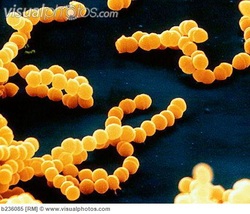
2) Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Gram-Positive, alpha/beta hemolytic member of Genus Streptococcus.
Sources: https://classificationofthekingdoms.weebly.com/eubacteria-examples.html
Archaebacteria
1) Thaumarchaeota
Memeber of the hyperthermophilic phylum Crenarchaeota.

Source: https://www.eurekalert.org/multimedia/pub/98139.php
2) Euryarchaeota
Highly diverse phylum of archae, produces methane and often found in intestines.

Source: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euryarchaeota
Protista
1) Radiolaria
Microscopic prozota that produce intricate mineral skeletons.

Source: https://www.radiolaria.org/
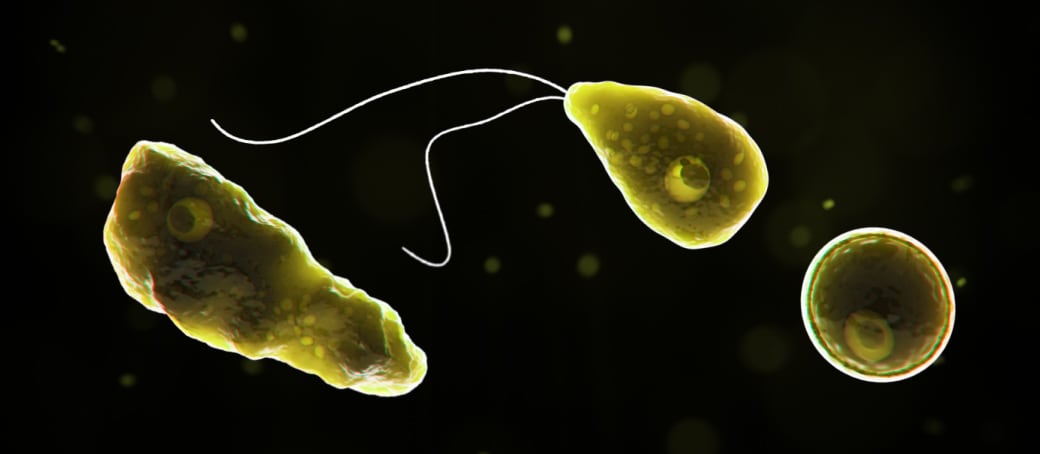
2) Naegeria Fowleri (Brain Eating Amoeba)
Species of the genus Naegleria, bacteria eating amoeba that can be pathogenic.
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/naegleria/index.html
Fungus
1) Ascomycota (Sac Fungi)
Largest phylum of fungi, with over 64,000 species.

Source: https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Ascomycota
2) Eomycota

Source: http://www.biodiversityexplorer.org/fungi/index.htm
Plant
1) Moss
Small flowerless plants that grow in dense groups.

Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moss
2) Chlorophyta (Green Algae)
Large grouping of Algae consisting of Chlorophyta and Charophyta.

Source: https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Chlorophyta
Animal
1) Tardigrade
Phylum of small “water bears” found in oceans.

Source: https://www.mnn.com/earth-matters/animals/stories/tardigrade-new-species-teach-us
2) Sponge
Member of the phylum Porifera, multi cellular animal that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them.

Source: http://www.worldanimalfoundation.org/articles/article/8948365/181984.htm