Question : How did the discovery of DNA prove that Darwin’s theory of evolution was correct and how does it change the way we view evolution today and into the future?
Darwin made his start on discovering the theory of natural selection on his five-year voyage on HMS Beagle from 1831 to 1836.  On September 15, 1835 on the return route across the Pacific, the Beagle arrived in the Galapagos Islands where Darwin would make his most notable discoveries. It was here on the Galapagos, that Darwin discovered the vast diversity of different animals on the islands, some species being exclusively located on the Galapagos, such as the finches he discovered.
On September 15, 1835 on the return route across the Pacific, the Beagle arrived in the Galapagos Islands where Darwin would make his most notable discoveries. It was here on the Galapagos, that Darwin discovered the vast diversity of different animals on the islands, some species being exclusively located on the Galapagos, such as the finches he discovered.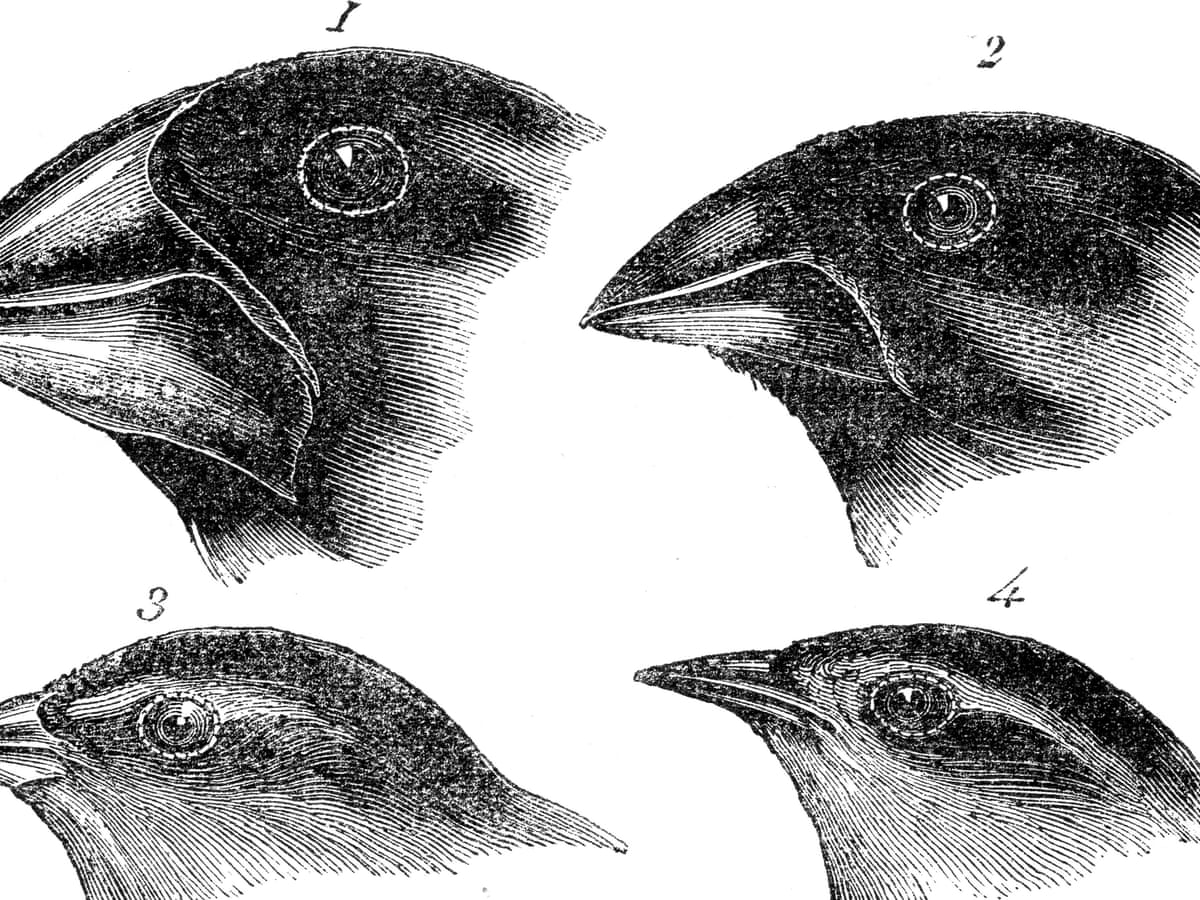 He noticed that different finches differ in the type of beak, depending on the island and how different tortoise species lived on islands with different environments, and that there were differences in their shells depending on their location. Darwin drew the conclusion that some species happen to change. Darwin began his study of dog breeder’s and how they were able to breed different dogs together to obtain a specific trait. All the evidence Darwin gathered led him to drawing his theory that ‘species can change over time, that new species come from pre-existing species, and that all species share a common ancestor.’ (khanacademy).
He noticed that different finches differ in the type of beak, depending on the island and how different tortoise species lived on islands with different environments, and that there were differences in their shells depending on their location. Darwin drew the conclusion that some species happen to change. Darwin began his study of dog breeder’s and how they were able to breed different dogs together to obtain a specific trait. All the evidence Darwin gathered led him to drawing his theory that ‘species can change over time, that new species come from pre-existing species, and that all species share a common ancestor.’ (khanacademy).
There were various pieces of evidence for Darwin’s theory of evolution at the time such as that of fossils. Fossils are preserved remains of organisms, often found in sedimentary rock. Fossils provide a record of how organisms evolved. nationalgeographic). hThis process of evolution can be visualized as a ‘tree of life’, showing that all species are related to eachother at a common ancestor, but branch off and evolve into different species. However, Darwin’s theory of natural selection, would be further solidified in 1953 with the discovery of the double helix DNA, by researchers James Watson and Francis Crick. With further investigation, it was discovered that many genes of DNA get translated into proteins that make up our bodies, and that DNA does not stay the same. This proves his theory that organisms are changing, and that there is a linear pattern that traces back to one common ancestor. DNA explains the patterns seen in homologous structures and provides even more evidence for Darwin’s theory of evolution. Some homologous structures can only be observed in the embryotic stages of development, but upon closer look, many organisms such as fish, humans, and birds share a similar homologous structure during the embryotic stage of development. 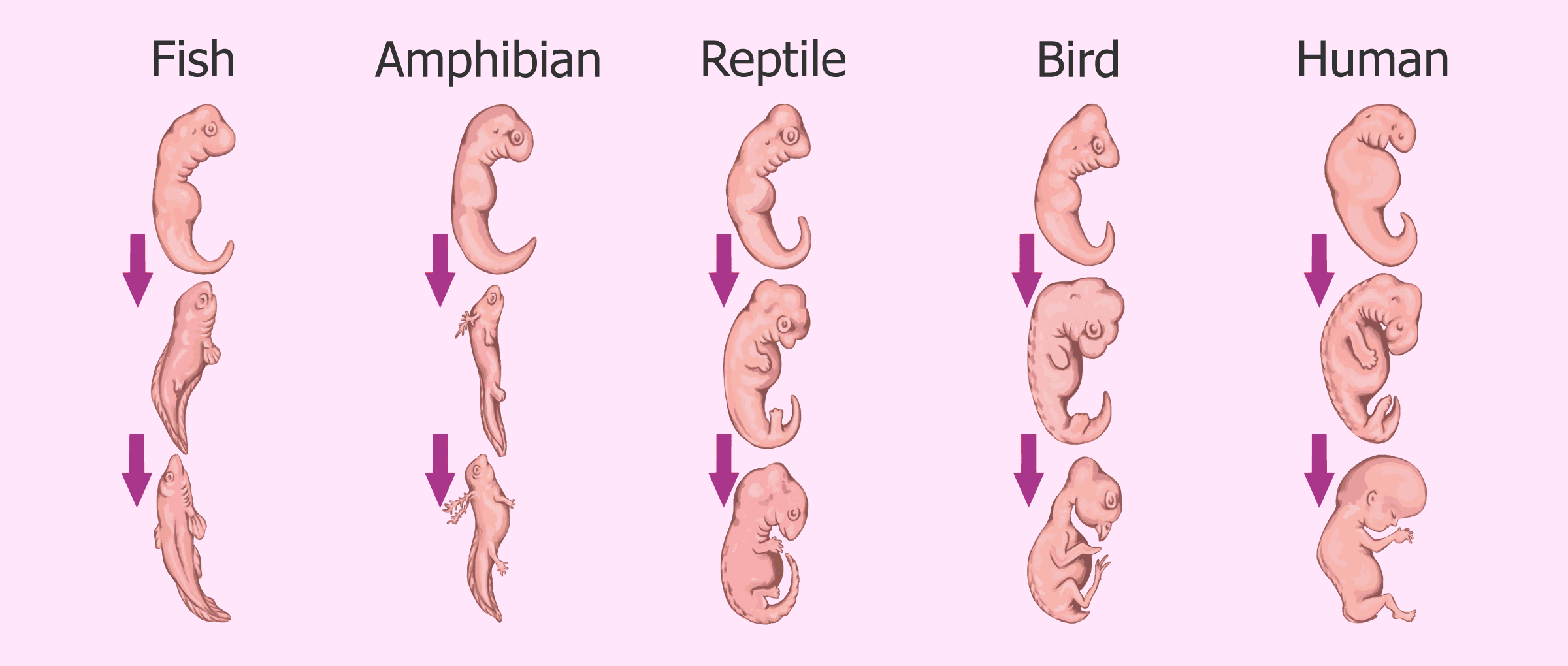 (biologyonline). For example, all vertebrate embryos have gill slits and a tail during early stages of development. The developmental patterns of these species begin to differ as development advances, which explains why the embryonic tail of a human is now a tailbone, and the ‘gill slits’ develop to become into the jaw and inner ear. These shared features suggest that all living things descend from a shared ancestor, and that this ancestor had DNA as its genetic material, used the genetic code, and expressed its genes. The reason that we do not still have our tail, and why we differ from birds or fish is due to Mutation. Hox genes encode transcription factors and are necessary during embryonic development for determining how the cells in a specific region develop, however all that is needed to determine if an animal has arms, or gill slits is a few mutations. This process entails a piece of DNA called a ‘switch’ that turns “on” or “off” genes. (What Darwin Never Knew). Genes are turned on and off in different patterns during development to allow for the differentiation of cells. This connects back to Darwin’s theory of evolution because it the reason that all species of life are related but evolve to become different. A great example of how mutations coded for a new species is that of many prehistoric fish, specifically that of the Tiktaakik.
(biologyonline). For example, all vertebrate embryos have gill slits and a tail during early stages of development. The developmental patterns of these species begin to differ as development advances, which explains why the embryonic tail of a human is now a tailbone, and the ‘gill slits’ develop to become into the jaw and inner ear. These shared features suggest that all living things descend from a shared ancestor, and that this ancestor had DNA as its genetic material, used the genetic code, and expressed its genes. The reason that we do not still have our tail, and why we differ from birds or fish is due to Mutation. Hox genes encode transcription factors and are necessary during embryonic development for determining how the cells in a specific region develop, however all that is needed to determine if an animal has arms, or gill slits is a few mutations. This process entails a piece of DNA called a ‘switch’ that turns “on” or “off” genes. (What Darwin Never Knew). Genes are turned on and off in different patterns during development to allow for the differentiation of cells. This connects back to Darwin’s theory of evolution because it the reason that all species of life are related but evolve to become different. A great example of how mutations coded for a new species is that of many prehistoric fish, specifically that of the Tiktaakik. (What Darwin Never Knew). It has the body of a fish with scales, but also the bone structure is seen in all four-legged forms. The fish evolved into what we know as modern-day land animals. However, some of the same bone structure remains between fish and land animals such as human. Another example is the biological composition of human and chimps. Chimps are human’s most closely related relative, with only a 1% difference in DNA. (What Darwin Never Knew) Once again, mutation is responsible for the evolution into different species. After the separation of ancestor lineages, human and chimpanzee genomes experienced various mutations such as single nucleotide substitutions, deletions, and duplications of DNA fragments of different size, insertion of transposable elements and the rearrangements of chromosomes. (Live Science). Differences in the sequences of DNA that turn genes on and off, and through sequences of the DNA that throw switches, is what is responsible for the large changes of different organisms, despite only small differences in the DNA molecule itself. This shows how small differences in DNA can generate enormous change.
(What Darwin Never Knew). It has the body of a fish with scales, but also the bone structure is seen in all four-legged forms. The fish evolved into what we know as modern-day land animals. However, some of the same bone structure remains between fish and land animals such as human. Another example is the biological composition of human and chimps. Chimps are human’s most closely related relative, with only a 1% difference in DNA. (What Darwin Never Knew) Once again, mutation is responsible for the evolution into different species. After the separation of ancestor lineages, human and chimpanzee genomes experienced various mutations such as single nucleotide substitutions, deletions, and duplications of DNA fragments of different size, insertion of transposable elements and the rearrangements of chromosomes. (Live Science). Differences in the sequences of DNA that turn genes on and off, and through sequences of the DNA that throw switches, is what is responsible for the large changes of different organisms, despite only small differences in the DNA molecule itself. This shows how small differences in DNA can generate enormous change.
Today we view evolution as an accepted part of science, as the process of gradual change that takes place over many generations where traits are passed from parent to offspring (nature). Darwin can be credited for pushing to dismantle the idea that all organisms on earth are created by God, but rather have evolved over time and come from a common ancestor. Darwin’s theory along with the discovery of DNA provides a strong foundation for the future study of evolution. With the discovery of DNA, our understanding of genetic mutations such as microcephaly, will continue to revolutionise science and will aide in solving some of the greatest mysteries to date regarding evolution and DNA as science advances.
Sources :
https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/evolution-78/
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/natural-selection/natural-selection-ap/a/darwin-evolution-natural-selection
https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/fossil/
https://www.biologyonline.com/dictionary/homologous-structures
https://www.livescience.com/15297-chimps-humans.html
Youtube : ‘What Darwin Never Knew”