Animalia
Pink Fairy Armadillo
Scientific Name: Chlamyphorus truncatus
The pink fairy armadillo found in central Argentina, is a member of the Animalia Kingdom.
It is a multicellular organism, meaning it has multiple cells unlike a unicellular organism. It is also an eukaryotic organism, meaning it has an organized nucleus with a membrane. It is also a heterotroph organism, which means it consumes other organisms to survive.

Another example of a member of the Animalia Kingdom is the
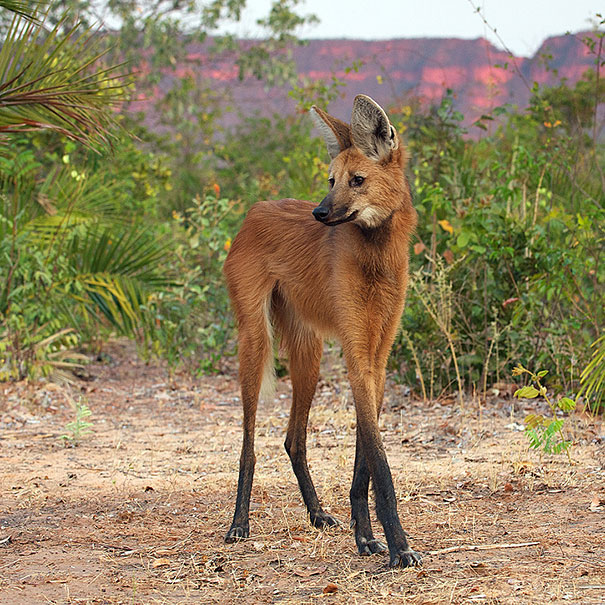
The Maned Wolf
Scientific Name: Chrysocyon brachyurus
It shares the same traits as the Pink fairy armadillo.

Plantae
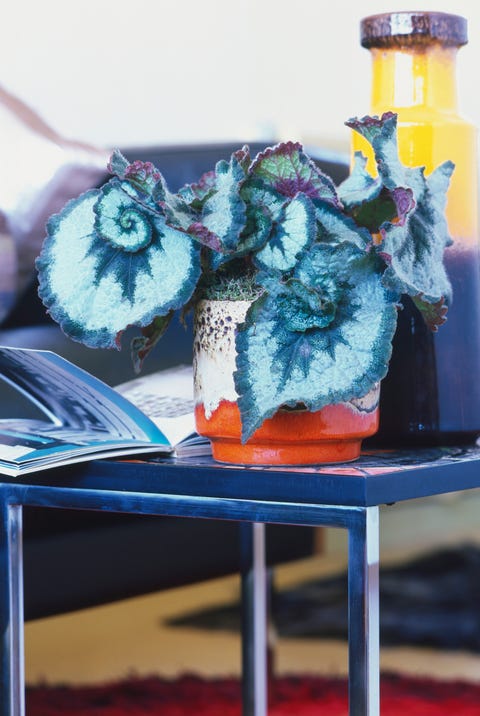
Rex Begonia
Scienctific name: Begonia rex
The Rex Begonia is part of the Plantae Kingdom.
It is a multicellular organisme and an autotrophic organism, meaning it has multiple cells and creates its own food.

Another example of a member of the Plantae Kingdom is the
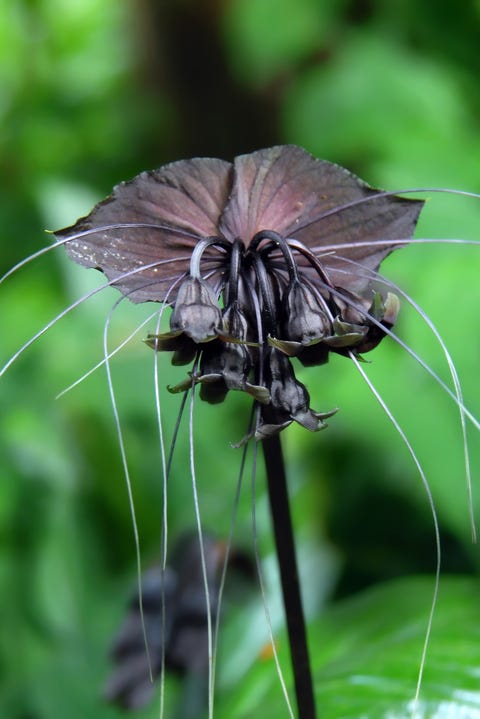
Bat Flower
Scientific Name: Tacca chantrieri
It shares the similar traits of the previous plant.

Fungi
Sac Fungi
Scientific Name: Ascomycota
Sac Fungi are hetrophobic, (they are decomposers). They are also Eukaryotes, which mean they do have an organized nucleus with a membrane.
 Another example of a member of the Fungi Kingdom is the
Another example of a member of the Fungi Kingdom is the
Eomycota
Scientific name: Eomycota
Shares similar traits to the previous fungus.
Protist
Amoeba proteus
Scientific Name: Amoeba proteus
The Ameoba proteus is found on decaying bottom vegetation in freshwater areas, its is also a heterotrophs and unicellular organism.
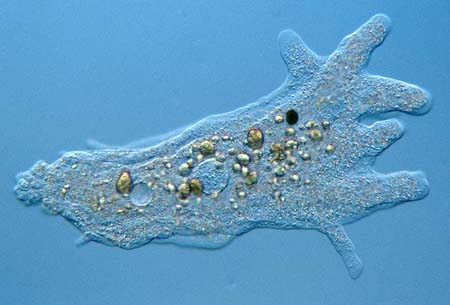
Another example of a member of the Protist Kingdom is the
Golden algae
Scientific Name: Chrysophyceae

Eubacteria
Bacillus
Scientific Name: Bacillus
Bacillus is a member of the Eubacteria Kingdom, its a bacteria. It is Prokaryotic which means it does not contain a nucleus any membrane-bound organelles

Another example of a member of the Eubacteria Kingdom is the
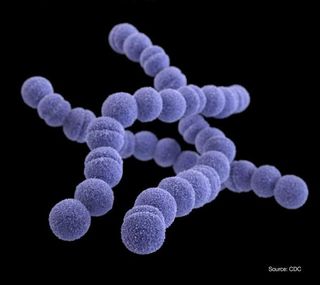
Streptococcus
Scientific name: Streptococcus
Shares similar traits to the bacteria above
Archaebacteria
Archaeoglobus fulgidus
Scientific Name: Archaeoglobus
Archaebacteria are unicellular prokaryoates with no cell nucleus.

Another example of a member of the Archaebacteria kingdom.
Halobacterium salinarum
Scientific Name: Halobacterium salinarum
Similar to the above organism

