The invertebrate I chose was the Coconut Crab.
Browsing category archives: Life Science 11
What Darwin Never Knew-Life Science 11
Charles Darwin was an outside-of-the-box thinker during his time, and questioned what we really knew back then about evolution and the origin of our species. He made his first discovery in Argentina, which would turn out to be a very influential discovery. He discovered that certains kinds of finches and tortoises on the Galapagos Islands differed in certain characteristics, depending on which island they lived upon.
As he came to the conclusion that although these birds and tortoises were the same, the species had adapted to suit whichever island they lived on. He also studied dog breeders, and how the best specific traits from both parents were passed down. This is called natural selection, and the pattern was that the creatures that survived were the best suited to the environment they lived in. Each generation would have varied characteristics, that would allow the fit to remain fit and the less fit to die off or vanish. During his time on the islands, he managed to find enough research to publish the book, “On the Origin of Species,” . This book also shared his research and discoveries that not all DNA stayed the same. The genes that passed on would mutate, and result in genetic change. An excellent example of this would be whales. Whales still have vestigial organs, which are organs they were born with, but have no use for. Whales have hipbones in their bone structure, seeing as they use to roam on the land instead of water. Now, whales are completely adapted to the water environment, and have no use for hipbones anymore. 
This can help explain why the bones of the human ear developed from fish gills, and that prehistoric fish eventually evolved to provide us now with the genes for arms and legs. While humans have been distantly related from fish, humans shared a 1% difference in the DNA of humans and chimps. The differences in the DNA sequences were in the switch gene, which were in a gene that involved the brain. The brain is one of the signature human organs, and the other one is the hands/thumbs. 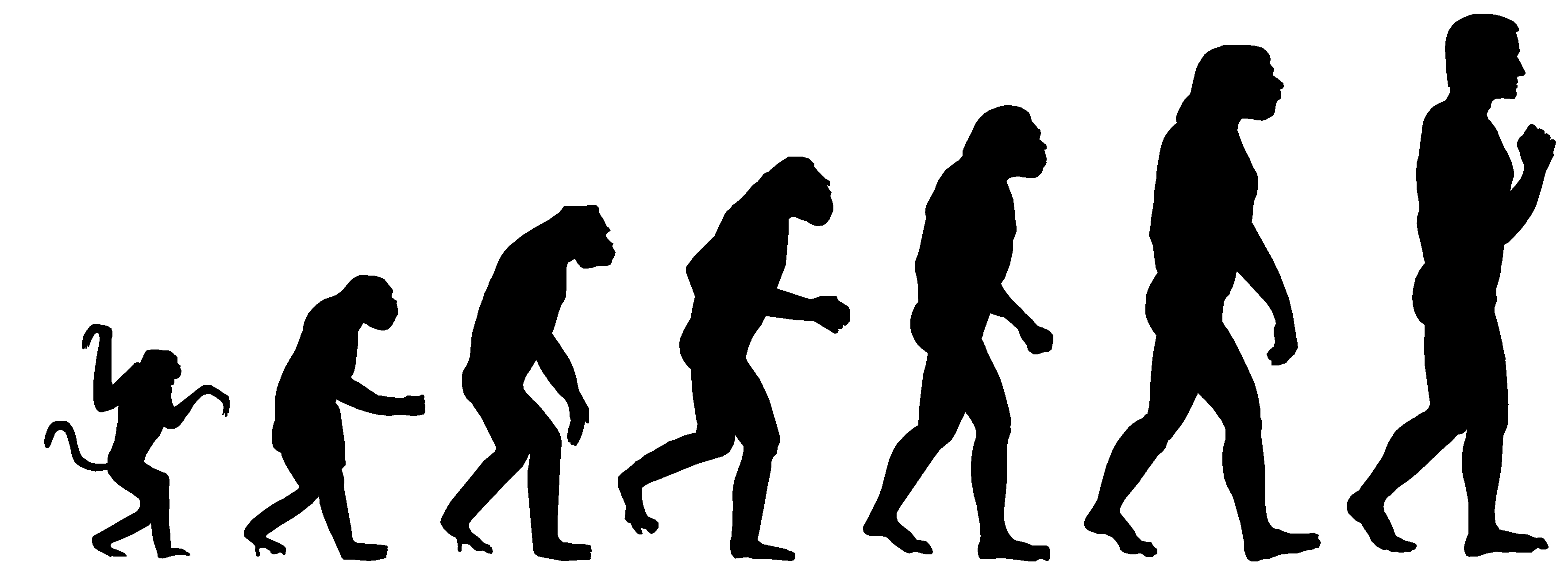
In conclusion, Charles Darwin’s discovery and research put into DNA can help prove that humans did in fact evolve from fish, and knowing that, we can trace back the in-between stages of humans and fish. Today, we can understand that chimps and humans are very closely related, and we can’t help but wonder if the chimps will evolve to be able to preform some of the functions we also do.
Image 1 from Socratic.org
Image 2 from Owutranscript.com
Life Sciences 11-6 Kingdoms
Each Kingdom has 2 examples and reasons of why I categorized these organisms as such. All images are from google.
Kingdom 1. Eubacteria
Spirillia fits into the Eubacteria kingdom because it has the ability to cause diseases and it can live in any place that is poor in sanitation or can be found in raw and uncooked poultry and meats.
Cocci also fits in the Eubacteria kingdom because it causes abcesses, boils and other infections of the skin. It doesn’t always causes disease, but it is responsible for causing pnemonia and mengingitus. Another version of bacteria also originates in the throat or skin and causes strep throat and scarlet fever.
Kingdom 2. Archaebacteria
Euryarchaeota (Archaeglobus fulgidus) fits into the Archaebacteria kingdom because it produces methane and lives in water with a high salt level, which is an extreme conditon.
Another example is crenarchaeota, (Acidilobus saccharovorans), which can live in extreme temperatures or in locations with extreme acidity.
Kingdom 3. Protista
An amoeba is an example of a protist because it moves by changing its shape and also lives in aquatic or moist environments. An amoeba also can be parasitic.
Sporozoans (Plasmodium) is also a protist because it causes malaria in humans, and can be classified as being parasitic. They do not posess structures that can move, and instead feed off their hosts to live. They also alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Kingdom 4. Fungi
Yeast is an example of a fungi because it can be found in pharmacies used in probiotics to help protect human’s against harmful diseases. However, it can also cause yeast infections in humans with a low immune system, which can be harmful if it gets in their bloodstream. 
Mold is also an example because it was used to produce penicilin and to make cheese. Mold can contaminate starchy foods, and it can also be found on fruits and old bread. When this mold is ingested it can be very harmful and cause cancer and birth defects. Many kinds of fungi can be dangerous and beneficial to humans at the same time.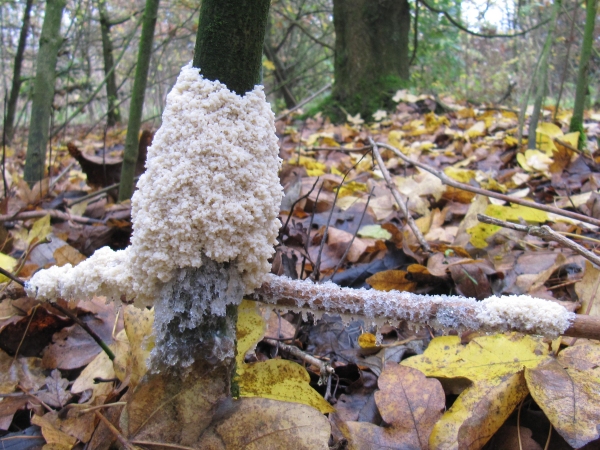
Kingdom 5. Plantae
An Angiosperm (mango/apple/grass) is an example of a plantae because it produces flowers and it is also an autotroph, which is a plant that prepare their foods, which are most green coloured plants. They also have chloroplasts and mitochondria in order to photosynthesis and thus are multicellular.
Another example is moss. Moss is an example because it is a eukyarotic organism that reproduces through the formation of spores. It is also an autotroph and prepares their own food, since it is a green coloured plant. Moss also have chloroplasts and mitrochondria and it is multicellular.
Kingdom 6. Animalia
An example is in the Phylum Mollusca category. These are multicellular and are in charge of finding their own food, making them heterotrophs. They can sexually reproduce and are an important part of the ecosystem. They also breathe oxygen, consume organic material, and are able to move.
Another example is the Ladybug, which is in the Phylm Anthropoda. These are also multicellular and eukaryotic. They are in charge of finding their own leaves to eat, and are hetertrophs. Since they breathe oxygen and are able to fly and move, they are in the Kingdom Animalia. They also are able to sexually reproduce by laying eggs.

