“The Cage” by Ruth Minsky Sender.
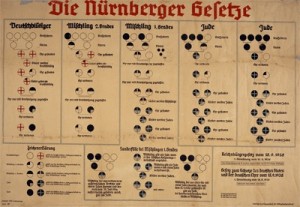
September 15, 1935- Nuremberg Race Laws against Jews are decreed.
History: On September 15, 1935, the Nazis declared the Nuremberg Race Laws. These laws carried out the Nazi ideology on the Jewish people, prohibiting them from owning businesses, possessing a Reich citizenship, and having sexual relations with those of German or German-related blood, along with many others. The Laws also stated that being Jewish was no longer dependant on religious beliefs or practicing Jewish customs, but was instead dependant on how many Jewish grandparents one had, for if one had 3 or more Jewish grandparents, they would be considered Jewish.
Nazi Germany Nuremberg Laws
Source: http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/Holocaust/nurlaws.html
Application: The Nuremberg Race Laws came into play early on in the novel and dramatically changed Harry and Mrs. Gruber’s perception of the Jewish people. The Laws state that being a Jewish person is no longer dependant on religion or practices, but instead on blood and genetics. Because of the imposition of these new laws, Mrs. Gruber and Harry begin to search through their own genetic heritage, looking for any source of German blood to protect them from the Nazis. When they do, they quickly betray Riva’s family for their “fatherland” and destroy their good friends home, taking everything with them. Although they had practiced Jewish customs with Riva’s family their whole lives and Riva considers them family, their perception changed at a blink of an eye. These dramatic personal changes are evidence that Harry and Mrs. Gruber are dynamic characters.
September 1, 1939 – Nazis invade Poland
History: When Germany invaded Poland, in 1939, the Polish army was defeated within weeks. Soon after, from Germany in the north and Slovakia in the south, more than 2,000 german tanks and 1,000 German planes swarmed the Polish border, and once through, proceeded to conquer Warsaw by means of a gigantic encirclement attack. On September 27th, 1939, Warsaw surrendered.
German soldiers parading through conquered Warsaw, Poland.
Source: https://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/article.php?ModuleId=10005070
Application: The German invasion of Poland, Riva’s native country, is the exposition to the novel, that sets the stage for Sender’s story. She describes the Germans invading Jewish households, beating, killing, and torturing thousands of people. The invasion of Poland in the novel sets the tone of the novel early on as well, preparing the reader with a glimpse of the excruciatingly difficult living conditions and punishments seen as the story progresses. It provides the reader with a bit of a physical setting as well, with the location and date mentioned between the lines.
October 26, 1939 – Forced labor decree issued for Polish Jews aged 14 to 60.
History: After Germany had conquered Poland and instituted a general government, the German authorities required Polish Jews to live in ghettos and gave them manual forced labor. In the Lodz ghetto for example, the Germans established 96 factories to contribute resources to the Germans in war. For many Jews, these menial tasks were enough to survive and receive some rations to support themselves and their loved ones. However if one was deemed unfit or no longer able to work, they would be the first to be shot immediately or sent to a German death camp.
Prisoners doing forced labor in the Ravensbrück concentration camp.
Source: https://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/article.php?ModuleId=10005180
Application : After the Lodz ghetto was established, the inhabitants trapped inside, including Riva and her family, were required to work in factories for the Germans. Riva for example, is given the job of braiding and rolling scraps of fabric into larger rolls that are then to be used in the fabrication of rugs for Germans. However since she is considered a “home worker” by the Nazis, she is not entitled to the soup given out the factories, and relies on Motele and Moishele to save their portions of soup to share all together. The making of rugs for the Germans may also be considered an internal struggle, or person against self conflict. Although Riva does not support the Germans in the slightest and would never provide for the enemy, she must braid and roll the fabric in order to live, perhaps prompting a moral debate within herself.
November 23, 1939 – Yellow stars required to be worn by Polish Jews over age 10.
History: In late fall, 1939, the Nazis imposed the idea that the Jewish badge, the star of David, be worn by all Jews over the age of six. The Nazis forced Jews to wear the badge to facilitate segregation and to give the Jews a sense of humiliation. The badge would be easily recognizable to the Germans in order to make deportation quicker and simpler. Children under the age of 6 were not required to wear the star however, as the Nazis believed as the children would follow their parents, who would be wearing the star, the children would be associated with their parents.
Young boy wearing star of David
Source: http://www.rhodesjewishmuseum.org/history/holocaust
Application: The star of David makes an important appearance in chapter four of Sender’s memoir, as Riva asks her older friend Saba if she feels shame in wearing the star on her clothing. Bewildered, Saba explains to Riva there is no shame in wearing the yellow piece of cloth as it represents the Jewish people, and that they should be proud to be Jewish. She talks about how the only ones who should feel shame are those who force others to wear it. This not only demonstrates to Riva the importance in being yourself, but gives hope to both Riva and the reader by contributing to an optimistic, hopeful tone to the chapter amidst all the violence and chaos.
January 25, 1940 – Nazis choose the town of Oswiecim (Auschwitz) in Poland near Krakow as the site of a new concentration
History: Auschwitz, or Auschwitz-Birkenau, was the largest of the Nazi concentration camps, located in southern Poland. Opened in 1940, The labor camp was originally made to serve as a detention centre, it became one of the most notorious and well-known Nazi death camps of WW2. The complex camp was made up of three main camps, all of which used prisoners for forced labor. One of the three camps, Auschwitz I, was the centre of Nazi enemy extermination, with more than one million individuals dying from gas, starvation, torture, labor, and medical experiments. The camp was liberated on January 25th, 1945.
Auschwitz entrance gate
Source: http://www.cnn.com/interactive/2015/01/world/auschwitz/
Application: In the novel, life in the ghetto becomes increasingly difficult, to the point that Riva, Motele and Moishele must leave the ghetto. With Mrs Boruchowich, Laibesh, Rifkele and others by their side, they leave their home behind, and head for the wagons, where they are then filed into train cars to Auschwitz, although they are not aware of their potential destination, nor the horrors within the gates. When they arrive, Riva is immediately seperated from her brothers and shoved alongside uncountable other women into the camp. She proceeds to have her head shaven, and is stripped of her clothing, receiving in return not anything but a scrap of cloth with which she is supposed to cover herself up with. Riva is brutally marshalled into a brief shower with the other women as well, and is required to take off her glasses so the metal can be used by the Nazis. At the end of part one, Auschwitz is presented as the new physical setting leading to part two of the memoir.
April 30, 1940 – The Lodz Ghetto in occupied Poland is sealed off from the outside world with 230,000 Jews locked inside.
History: After Germany invaded Poland, they occupied Lodz one week later, renaming it Litzmannstadt, after the German general. The Germans soon instituted a ghetto in the northeastern section of Lodz, housing 230,000 Jews inside, and moving a third of the Lodz population into a small area. The invaders then isolated the ghetto from the rest of Lodz with special security police manning the perimeter. Internal order within the ghetto was to be maintained by the Jewish ghetto police.
Lodz ghetto, Poland 1940-1941
Source: https://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/article.php?ModuleId=10005071
Application: The Lodz ghetto plays a pivotal part in Ruth Minsky Sender’s memoir, as it is the main physical setting for the majority of part one of the novel. After Lodz is invaded by the Nazis, Riva and her family find themselves a part of the newly founded ghetto. Living conditions are unimaginable, and after Riva’s mother is taken away, she is now required to be her younger sibling’s legal guardian. In the ghetto, very little comes in and out, and Jews are taken from their homes on a consistent basis. Education is non-existent, and work is very hard to come by. Food in the ghettos is far and in between, with many dying of starvation and no resources to regain one’s health. For example Laibele becomes sick, but with nobody able to provide a cure, he dies shortly after. Near the end of the chapter, many of the inhabitants are even required to leave their home to file into Nazi trains, as surviving in the ghetto is no longer an option.