For the final project of science 9 we have learned about cellular reproduction and mitosis and meiosis.
Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction is a a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle. The cells have a single set of chromosomes and a diploid phase composed of cells with a double set of chromosomes. During sexual reproduction the male sperm may be placed inside the female’s body for internal fertilization. The sperm and eggs may be released into the environment for external fertilization. Examples

Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism and they inherit the genes of that parent. It does not involve the fusion of gametes and almost never changes the number of chromosomes.
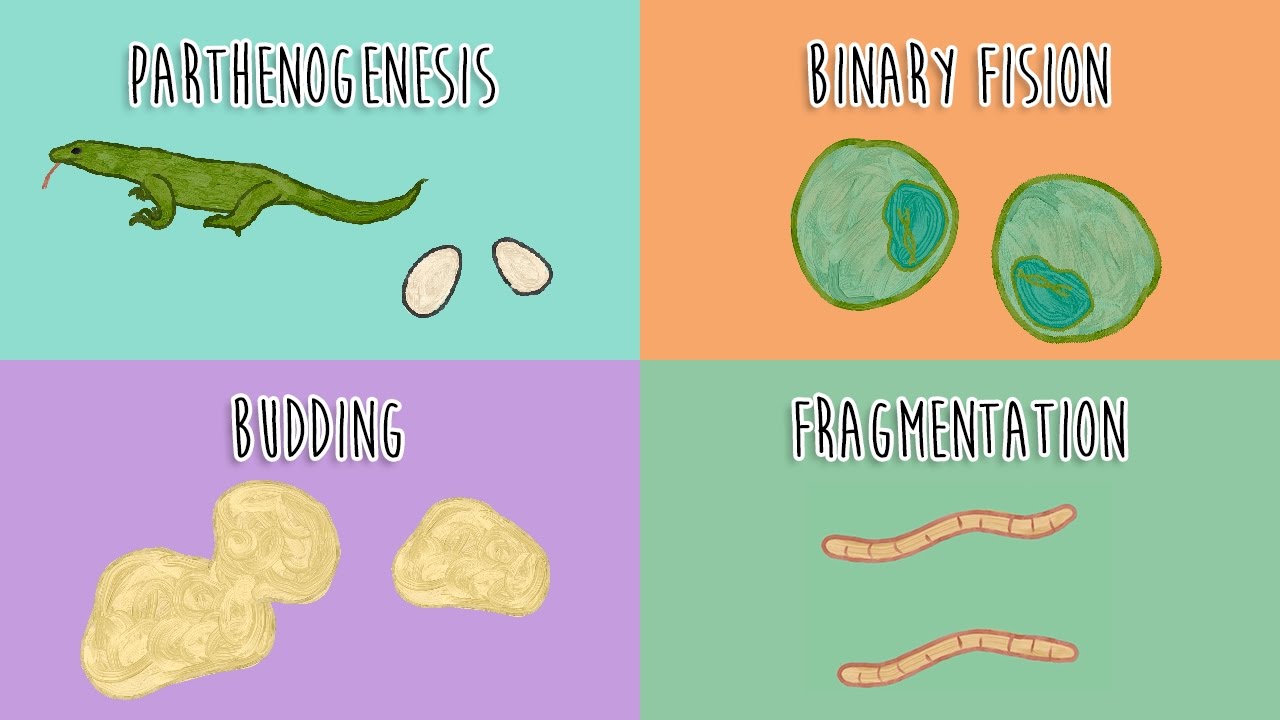
Types of asexual reproduction:
Binary Fission: Single cell organisms splitting into identical properties.
Fragmentation: part of an organism breaks off due to injury.
Budding: Detach to from a separate organism.
Vegetative Reproduction: Special cells in plants that develop into structures that from new plants.
Spore Formation: single cells that can grow into a whole new organism.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle where replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. The cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the number of chromosomes is maintained.
Examples:
In unicellular organisms such as bacteria, mitosis helps in asexual reproduction. Another example of the no nuclear organism is Amoeba. An amoeba uses cell division for the production of new individuals.
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division used by sexually reproducing organisms to produce sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome.
What is the difference between Meiosis and Mitosis?

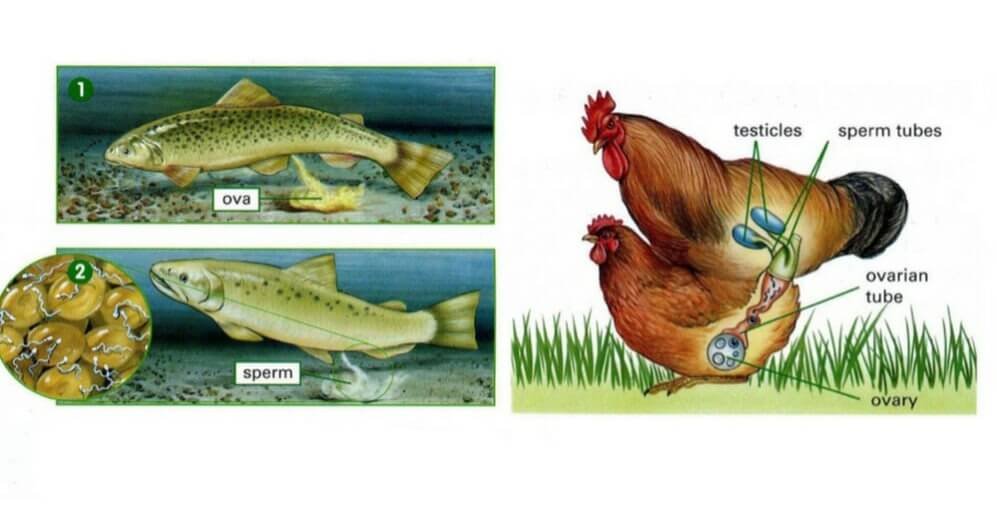
What is the difference between external and internal fertilization?
external fertilization: This type of fertilization is common with animals that live in water and with plants that live in moist environments.
internal fertilization: This type of fertilization is common with birds, mammals, and flowering and cone-forming plants.
How does the embryo develop?
Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly and tissues and organs form. During the first week the single fertilized cell develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells then hollows out and is called a blastula.
What happens during fetal development?
After the first eight weeks of development the embryo is called a fetus. During fetal development the organs and parts of the body continue to develop. The body adds a great deal of weight. At birth the human baby is made up of trillions of cells.





