Category: Grade 12
Neuron and Synapse Anatomy & Physiology
Neuron Diagram

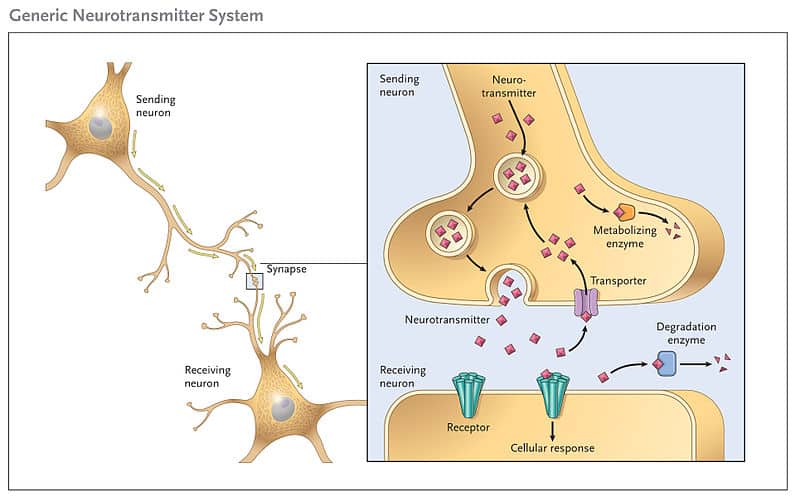
Neurotransmitter and Synapse

___________________________________________________________________
Functions:
Dendrites- At a start of a neuron, its job is to transfer impulses and messages throughout the neuron. Carries impulses to cell body
Axon – Located at the end of a neuron, carries impulses away from cell body
Cell body- Carries genetic information, maintains structure of neuron and provides energy
Myelin Sheath – fatty material that covers and speeds up electrical impulses in myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier- Small spaces in between the myelin sheath, helps create rapid conduction of nerve impulses
Terminal branches of axon–contain synaptic vesicles that store the neurotransmitter for release at the synapse
How do neurons carry messages & communicate with each other?
They communicate by the release of neurotransmitters from the axon into the synapse. This creates action potential and electrical currents
_____________________________________________________________________
Synapse structure & function:
How a signal is sent from axon of sending neuron to dendrite of receiving neuron-
Electrical impulses in the neutrons cause the current to move down the axon to cause a release of neurotransmitters to the synapse. The neurotransmitters bind to Receptors (located on Dendrites), where receptors receive and process messages.
How the receiving neuron “determines” whether or not to send its own action potential-
Dendrites receive electrical currents from the axon, the charge/action potential is determined by how the neutron will be fired. When a neutron is fired across a synapse, then action potential will be created.
______________________________________________________________________
Glia structure & function:
What does Schwann cells do & where found?
Schwann cells are found in in the Myelin Sheath. They’re job is to keep peripheral nerve fibres alive.
- What does Astrocytes do & where found?
They are found in the brain and spinal cord. Astrocytes are meant to regulate electrical impulses within the brain.
What does ependymal cells do & where found?
Ependymal cells is for the maintenance of homeostasis in the brain and retinal extracellular milieu and for the formation of the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier or the blood–retina barrier. They are found in the brain and CNS (Central Nervous System).