6 Kingdoms Assignment/Bio 11
1. Kingdom Archaebacteria

- Desulfurococcus kamchatkensis
Desulfurococcus kamchatkensis is isolated from a terrestrial hot spring of Uzon Caldera (Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia). It is able to grow at temperatures between 65 and 87 degrees Celsius. A reason as to why Desulfurococcus kamchatkensis is part of kingdom Archaebacteria is because it lives in a harsh environment. (Thermoacidophies) to be exact. Which means a hot place. In this case, hot springs.
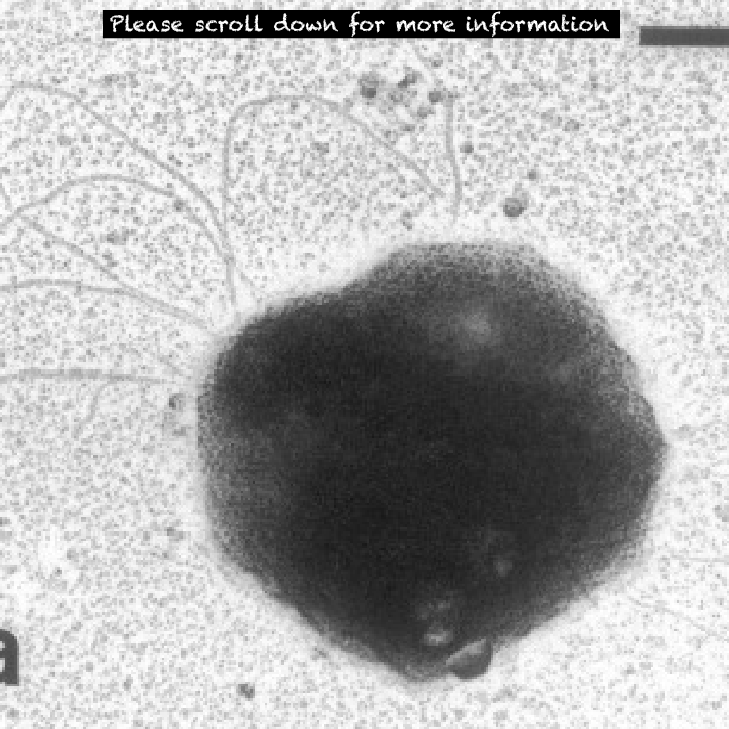
2. Hyperthermus butylicus
Hyperthermus butylicus was isolated from the sea floor of a solfataric habitat with temperatures of up to 112 degrees C on the coast of the island of São Miguel, Azores. The organism grows at up to 108 degrees C. A reason as to why Hyperthermus butylicus is part of kingdom Archaebacteria is because it also lives in a harsh environment. (Halophiles) because it is from the sea.

2. Kingdom Eubacteria
- Streptococci
Streptococci cause many disorders, including pharyngitis, pneumonia, wound and skin infections, sepsis, and endocarditis. “Streptococcus” derives from a Greek term meaning “twisted berry” and refers to the way the bacterium is grouped in chains that resemble a string of beads. A reason as to why Streptococci is part of kingdom Eubacteria is because it causes diseases.
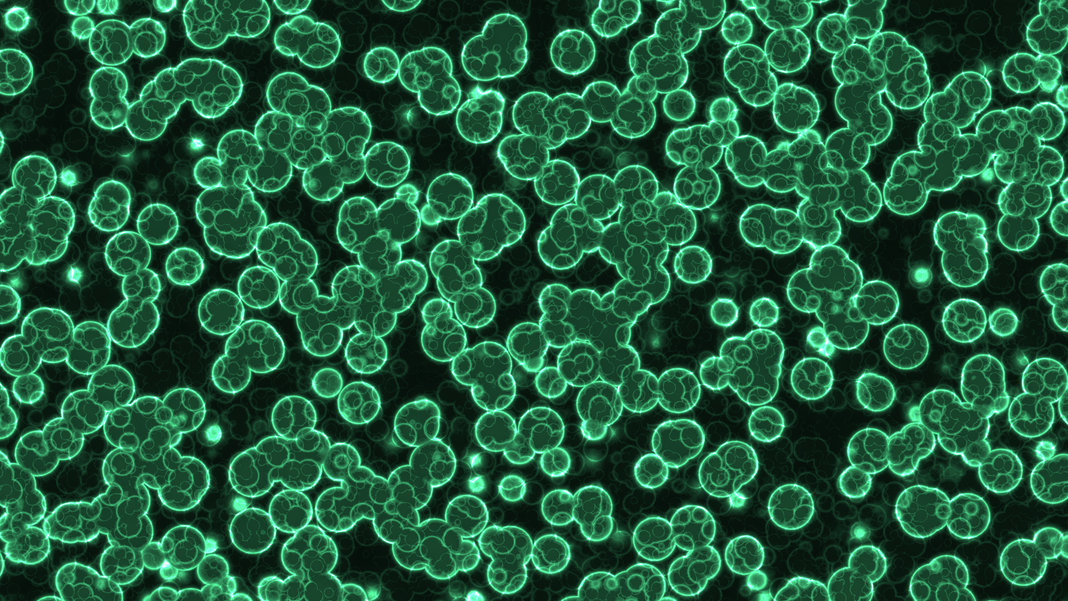
2. Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis. They are the only photosynthetic prokaryotes able to produce oxygen. Some species of cyanobacteria produce toxins that affect animals and humans. Cyanobacteria can be found in almost every terrestrial and aquatic habitat, oceans, fresh water, damp soil, temporarily moistened rocks in deserts, bare rock and soil, and even Antarctic rocks. A reason as to why Cyanobacteria belongs to kingdom Eubacteria is because it causes diseases and because it lives almost everywhere.
3. Kingdom Prostita

- Paramecium aurelia
Paramecium aurelia are unicellular organisms. They are covered in cilia which help in movement and feeding. Paramecium can reproduce sexually and asexually. Paramecium aurelia can also make humans sick. A reason as to why Paramecium aurelia would be part of Kingdom Prostita is because it causes sickness and because it is unicellular.
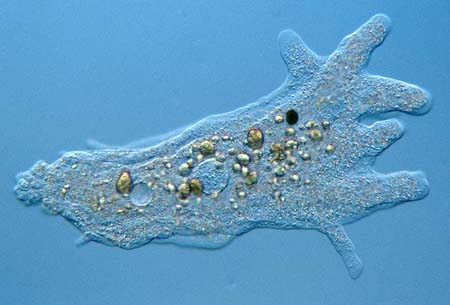
2. Amoeba proteus
Amoeba port proteus has an ever changing shape and is approximately 500-1000µnm long. It can almost be seen with the naked eye. Also infectious with humans. It occupies freshwater environments and feeds on other protozoans, algae, rotifers, and even other smaller amoebae. Also unicellular. A reason as to why Amoeba proteus is part of Kingdom Prostita is because it is infectious and unicellular as well.
4. Kingdom Fungi

1. Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae and reproduce sexually. A reason as to why Basidiomycota is part of Kingdom Fungi is because it contains chitin (carb) in the cell walls and composed of hyphae (thin filament.)

2. Zygomycota
Approximately 1050 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Zygomycota are able to reproduce both sexually and asexually. A reason as to why Zygomycota is part of Kingdom Fungi is because it contains Mycelium. (Thick mass of hyphae.)
5. Kingdom Plantae
- Astragalus amphioxys

Astragalus amphioxys is a plant that is found in the American southwest. Astragalus is taken by mouth for the common cold, upper respiratory infections, seasonal allergies, swine flu, fibromyalgia, anemia, HIV/AIDS, and to strengthen and regulate the immune system. It is also used for chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), kidney disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. A reason as to why Astragalus amphioxys is part of Kingdom Plantae is because it needs sunlight, gas exchange, water/minerals, and movement of water and nutrients in order to survive
2. Glaucophyte

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater
unicellular algae. Green algae is often classified as part of the Kingdom Plantae. One reason being that they go through photosynthesis.
6. Kingdom Animalia
- Echinoidea (Sea urchin)

About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones. Sea urchins can be found all over the world in all oceans, warm or cold water. They live in a variety of environments in many different parts of the world. Some common places they live are in rock pools and mud, on wave-exposed rocks, on coral reefs in kelp forests and in sea grass beds.Reasons as to why they are part of Kingdom Animalia are that a) no cell walls b) reproduce sexually c) are multicellular. There are of course many more reason as to why sea urchins belong in this kingdom.

2. Glaucus atlanticus (Blue glaucus)
Glaucus atlanticus is a species of small, blue sea slug. They float upside down by using the surface tension of the water to stay up, where they are carried along by the winds and ocean currents. It lives throughout the world’s oceans, mostly in temperate and tropical waters. They belong to Kingdom Animalia because they have no cell walls, are multicellular, are motile and many other reasons.