Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction: is a process to make more organisms like themselves.
Asexual Reproduction
- it only needs one organism and results in offspring that are genetically identical
example: bacteria; splits into two called Binary Fission
- hydra can reproduce by Budding; they bud an identical offspring right off of themselves, it falls of and grows into a new hydra (not only hydra can do Budding). Becomes new independent individuals.
- part of an organism breaks off and the part grows into a clone of the parent called Fragmentation
example: sea star
Clones: an identical copy of its parent
3. Vegetative reproduction: special cells in plants that develop into structures that form new plants identical to the parent like potatoes
4. Spore formation: some microorganisms, bacteria and fungi can form spores- single cells that can row into a whole new organism.
Offspring is produced from single parent, without the involvement of sex cells or gametes
Sexual Reproduction
- when gametes unite to make a new organism
Sperm Cell from the Male organism; Testes produce sperm, the male gametes. Semen helps carry the sperm into the female reproductive system.
Egg cell from the Female organism; The female gametes are released from the ovaries. One is release every month by a process called ovulation. After ovulation, the egg travels along the tube called Fallopian tube.

When they combine, they can produce a new cell, a fertilized egg known as a zygote
- this mixing comes about because of sexual reproduction which involve the joining of two sex cells in the process called fertilization.
- this fertilized egg continue to divide to make more and more cells
In sexual reproduction, the offspring is not a clone. They received genetic information from two different parents. When they combine, they make a unique organism.
- More time consuming because it does require two gametes finding each other and uniting. Much complicated than asexual reproduction
animals (sexual and asexual reproduction)
- almost all animals go to the process called Sexual Reproduction
- some animals like humans go through internal fertilization, where the egg is fertilized inside the body, the offspring develop inside the mother.
- Some animals (ex: Fish) have external fertilization. The female releases her eggs then the male fish spreads his sperm over her eggs. The young develops outside the body.
- It doesn’t matter how the egg is fertilized, the offspring gets some genes from each parent.
- Sexually reproduced offspring are not identical to one another.
Pros and Cons of Asexual Reproduction:
Pros
Pro: No need to search for mate; requires less energy
Pro: it allows for species survival; instead of requiring a mate, the parent can simply clone itself.
Pro: Multiple forms of asexual reproduction are available
examples: budding, binary fission, fragmentation
Pro: Only one organism is required to establish a colony
Cons
- Cons: If the parent has a genetic disease, offspring dies too
- Cons: There can be an inability to adapt, asexual organisms are not always able to adapt to a changing environment or habitat
- Cons: Population numbers can be difficult to control
Pros and Cons of Sexual Reproduction:
Pros: The offspring’s DNA is unique or different
Cons: Takes time and energy to find a mate
Pros: Reduces the risk of genetic disease
Cons: Reproducing through sexual may not be successful
Pros: it allows for genetic diversity
Cons: Fewer offspring are typically produced
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis is a part of the cycle where the cells split up to create a new cell to replace the damaged cell or by making more new cells. Makes identical body cells like skin cells and stomach cells. Which is important for growth and repair for damage or to replace worn out cells.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stages-of-mitosis-373534-V5-5b84992cc9e77c00574f03d3.png)
Mitosis: nucleus contents duplicated and divided into two equal parts
starts with a cell that has a diploid number of chromosomes; chromosomes are made of DNA and protein
for human beings we have 46 chromosomes:
23 from your mother
23 from your father
- Shortest stage of the cell cycle where the nuclear contents divide
- has 4 stages (PMAT)
- Interphase happens before the process starts
- Interphase is when the cell is growing, replicating its DNA and carries out cell process
Early prophase: nucleolus disappears and spindle fibers form
Late prophase: spindle fibers attach to centromeres of chromosomes
Metaphase: The spindle has captured all the chromosomes and lined them up at the middle of the cell
Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell
Telophase: Spindle fibers disappear and a nuclear membrane forms around each separated set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis: is the separation of the nuclei into two daughter cells
After the process of Mitosis happens (you have every stages) you end up with two cells that each have the same genetic information as the original. You now have 2 cells that each have the diploid number of chromosomes. Each of those cells is the same as the first cell, it would undergo the process and stages, it goes to interphase again and it grows and it can replicate its DNA and centrosomes and grow some more. Then each of those 2 cells can grow again and undergoes the process. This is how most cells in your body grow.
After each of these, things go through mitosis and go through the entire cell cycle again.
Cell Problems: The cell cycle will prevent division if..
the DNA is damaged
the cell is short in nutrients
if the DNA within the nucleus is not damaged
Meiosis
Meiosis is a process that contributes to genetic variety. This does not make body cells, it makes sperm and egg cells which is also known as gametes. Human sperm cells and egg cells have 23 chromosomes. When each of the sperm and egg cell has 23 chromosomes, when they come together it makes 46 chromosomes that will allow a newly formed fertilized egg to develop into a human.
Interphase happens before the process starts! Just like mitosis, interphase happens before meiosis is going to start
- Interphase is when the cell is growing, replicating its DNA and carries out cell process
starting cell has 46 chromosoms, and you have to duplicate those chromosomes in interphase before meiosis starts. Which means you’re duplicating your DNA, since chromosomes are made of DNA and protein.

You do PMAT twice ( first division and second division )
MEIOSIS 1:
Prophase 1: the word “Pro” means “before” this will help you remember that it comes before all the other stages start. This is where the chromosomes are going to condense and thicken. They are going to line up with their homologous pairs. Homologous means that the chromosomes are approximately the same size and they contain the same types of genes in the same location. They are going to match up, this process occurs called crossing over. This is when the chromosomes are lined up in homologous pairs, they have this way where they can transfer their genetic information and exchange it between each other.
Metaphase 1: Think of the “M” as middle. The chromosomes are going to be in the middle of the cell. It’s a bit different from Mitosis because they’re still going to be pairs in the middle of the cell so its not a single fine line; they are in pairs in the middle.
Anaphase 1: Think of the “A” as Away because the chromosomes are going to be pulled away by the spindle fibers.
Telophase 1: Then we end with telophase, think of the “T” as Two because this is where you have 2 newly formed nuclei and it becomes obvious you will end meiosis one with two new cells
Cytokinesis follows with splitting the cytoplasm
MEIOSIS 2:
Prophase 2: this will not be the same as Prophase 1 because they are not going to have homologous pairs of chromosomes and they also are not going to have the process called crossing over. You have your chromosomes and the spindle fibers starting to form like prophase 1 but prophase 2 is not nearly as eventful of having that process of crossing over.
Metaphase 2: The chromosomes are going to line up in the middle, this time though, they’re going to line up in a single fine line. They are not in pairs like Metaphase 1.
Anaphase 2: “A” for Away. But this time, its the chromatids that are getting pulled away by the spindle fibers.
Telophase 2: nuclei reform and the 2 cells are each going to divide. The 2 cells have divided there’s going to be 2 cells forming
Cytokinesis will follow to completely split the cytoplasm.
MEIOSIS IN MALES PRODUCES SPERM CELLS: in a male, the four sperm cells that are produced each time are different from each other. This is going to lead to variety which is the reason why two siblings with the same parents can look different from each other.
MEIOSIS IN FEMALES PRODUCES EGG CELLS
the difference and similarities between Meiosis and Mitosis:
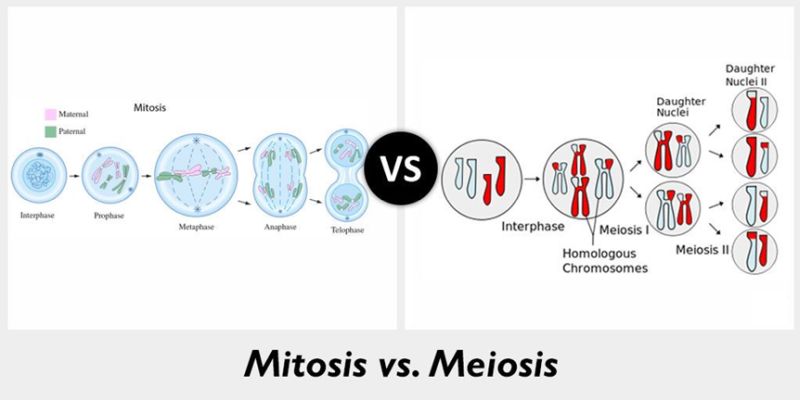
differences:
Mitosis:
- makes body cells like skin cells and stomach cell
- goes through the stages called PMAT
- Produces 2 diploid daughter cellls
Meiosis
- results in egg and sperm cells, known as gametes (makes gametes)
- goes through the stages (PMAT) twice, and therefore has a number next to each PMAT stages
- this have 8 stages since they have to go through it again (PMAT1 and PMAT2)
- produces 4 haploid daughter cells
similarities:
- meiosis and mitosis are involved in making new cells
- ways for cells to divide
- starting cell in both meiosis and mitosis is diploid, that means it has 2 sets of chromosomes.
- go through stages, in short PMAT but meiosis go through them twice; P1M1A1T1 and P2M2A2T2
- both goes through interphase before the process begins
how do organisms grow?
all types of organisms are capable of reproduction, growth and development. Just like you and me. Our cells keep dividing to produce new ones or to replace the damaged ones. From what we learned this is from the process called Mitosis. But before it can even produce new cells, everything that the cell needs must be met. If one of the cell is short in nutrients, the DNA inside the cell’s nucleus is not replicated, and the cell is damaged then the cells cant split up. If all of these are met, then the cells will continue to divide and produce new cells.
The first step for growth is mating. This is when the sperm and egg cells meet at the same time. From what we learned, there are two types of fertilization. External and Internal; from the word External, it means that the gametes meet outside of the parent’s body. With the word “Internal” it means that the gametes meet up inside of the female’s body. After this, the next step is that the growth of an organism is when the embryo develops, which happens during the first eight weeks.
There are three trimester; The first trimester is when all of the organs, like spinal cord and brain develop which happens in 4 weeks. The second one is when the bone cells start to form and the embryo is now called Fetus which happens in 8 weeks. Lastly, the fetus is still growing, like the brain. It will gain more weight so it can be ready for delivery. After all the process, the baby is going to be born.
sources:
Website called OneNote from our class that have a lot of useful information
The things I learned from Science9 Class
all pictures:
biologyreference.com
biologycK-12foundation.com
differencebetweenwikipedia.com
bestdifference.com
image.shutterstock.com
thoughtco.com

