Neuron Structure and Function:
A neurons function is to process and transfer information. Neurons are composed of a cell body, the largest volume section, dendrites in which conduct messages towards the cell body, fibres carrying incoming messages, and an axon conduct message away from the cell body, it takes the message from the cell body and sends it out to the next cell. There are 3 different types of neurons motor neurons, sensory neurons, and the interneurons. Each of these neurons all do different things but have different parts to it. The dendrites receive information from another neuron and other sensory receptors. The cell body is the center of the cell’s life support. The axon carries the neurons message to other areas in the neuron. Myelin coves the axon of the neuron. It helps speed up neural impulses, such as action potential. At the end of the axon, there are axon terminal buttons. The axon terminal buttons reach out and communicates with other neurons.
Action Potential:
An action potential happens when the certain neuron gets stimulated. Before the action potential happens, the neuron is in resting potential, meaning it is more negative on the inside with a charge of -70mV. The second stop of the action potential is depolarization. Depolorization is when incoming message stimulates section of the axon, channels in membrane open to allow Na+ ions to enter the axon, which is saying sodium (Na+) that was on the outside comes inside the neuron, making the charge +30mV. After depolarization, repolorization occurs allowing the potassium (K+) that was inside the neuron go on the outside, repolarization give the neuron a charge of -75mV. The last step of action potential is the recovery phase. During this last phase, the sodium on the inside of the neuron switches places with the potassium on the outside. Everything is returned to normal and ready for the next action potential.
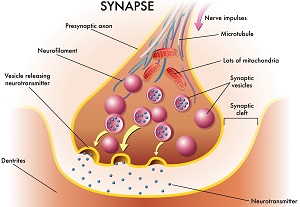
The Synapse Structure and Funtion:
The Synapse includes: tips of terminal branches of the axon, tiny spaces between neurons, the synapse is the space between the dendrite and the axon, ends of dendrites of receiving neuron. After the sending neuron has its action potential, the terminal buttons reach out and communicate with dendrites of the receiving neurons. When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons, the synaptic vesicles move towards the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters are then pushed into the synaptic gap, where they will move towards the postsynaptic membrane. If the neurotransmitter doesn’t make it there, they will be recycled and reused. Once in the post synaptic membrane, the neurotransmitters will go into the neurotransmitter receptors and notify the cell body that a message has been sent and the cell will decide whether or not to have its own action potential or not.
LINKS:
synapse structure and function



Leave a Reply