GENERALLY
Trigonometry definition:
trigonometry can be defined as simply as the mathematics involving the relationships between side lengths and angles of a triangle.
New vocabulary:
terminal arm: the line found within any of the 4 quadrants, creating an angle
coterminal angles: angles that share the same initial and terminal sides
quadrantal angles: angles that lie directly on the x and/or y axis (ie. 0°, 360°, 90°, 180°, 270°)
Rotational angle: the angle between 0° and the terminal arm
reference angle: the angle measured between the closest seperation of the x-axis and the terminal arm.
LESSONS SUMMARY
6.1 General updates-
Calculating the reference angle: ref angle= 180 – 92= 88°
calculating the coterminal angle: 
hypotenus=radius
sides= x & y
——>
6.2 Exact Trig Values
sin=y/r, cos=x/r, tan=y/x
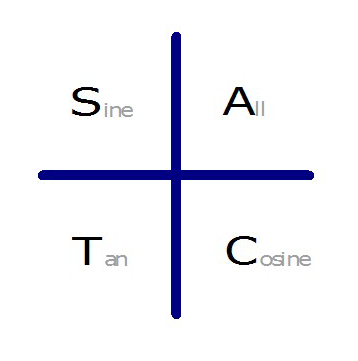
To remeber in which quadrants each ratio is positive: CAST rule
Special Triangles
originally a square:
originally an equilateral triangle:
The Sine Law
this formula can be modified so that the variable for which you are solving (either an angle or side) can be solved in fewer steps.
The Cosine Law
To be used if there are no angles with corresponding side lengths given and thus sine law will not work


